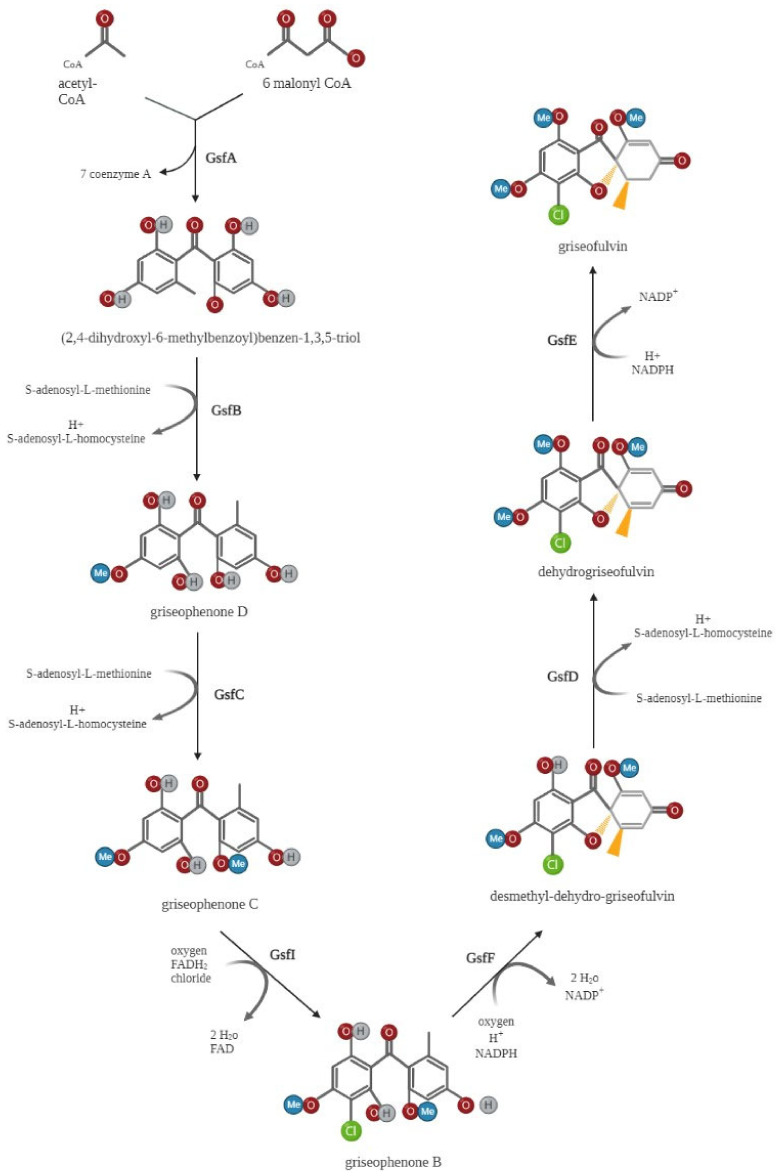
Figure 2.
Griseofulvin biosynthetic pathway. The nonreducing polyketide synthase gsfA initiates the synthesis of griseofulvin by combining one acetyl-CoA and six malonyl-CoA units to form the heptaketide backbone of benzophenone 5a. The O-methyltransferases (gsfB and gsfC) then methylate phenols on benzophenone 5a to generate the intermediate griseophenone C. Following this process, griseophenone C is chlorinated by the halogenase gsfI to produce griseophenone B, and griseophenone B is then converted to the grisan core by phenol oxidative activity of gsfF. The grisan core is ultimately converted into griseofulvin by two further processes: enoyl reduction catalyzed by gsfE and methylation at 5-OH mediated by gsfD. Created by Biorender.com.