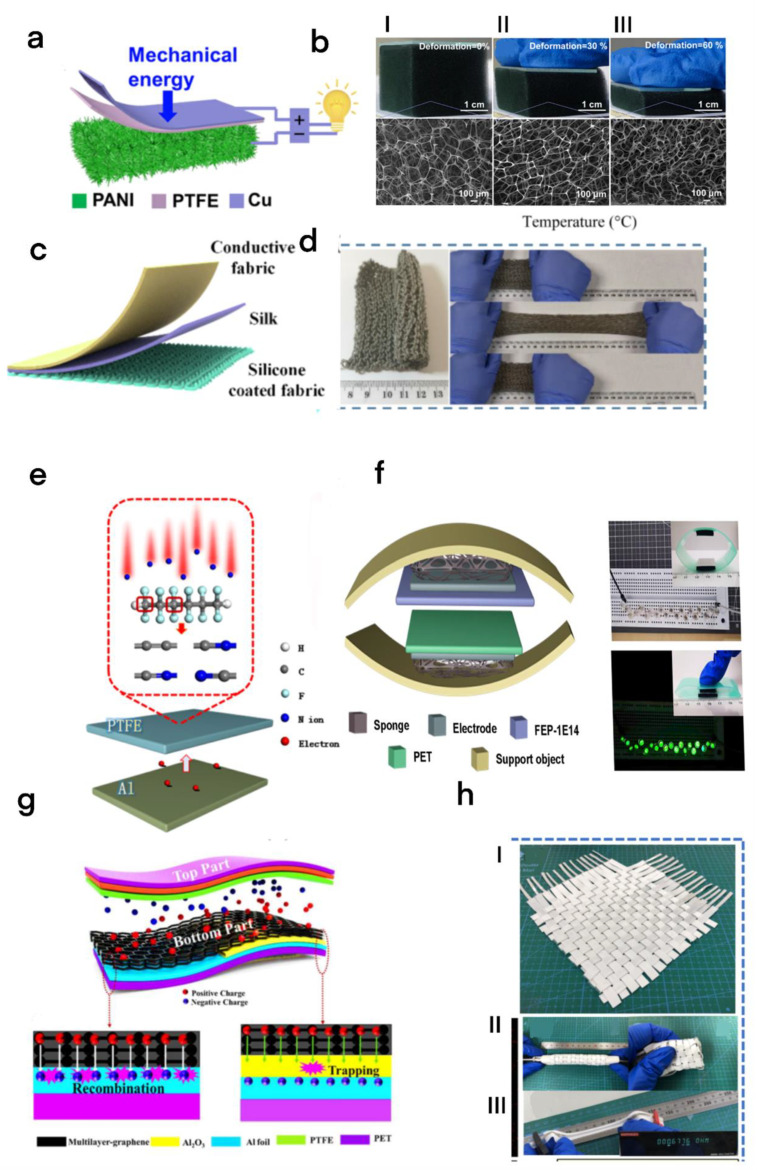
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic representation of the ES-TENG. (b) (I–III) The optical and SEM pictures of a conductive flexible sponge with various compressive strains [35]. Liu et al. (2020), Elsevier. (c) Fabric TENG device structure for collecting acoustic energy. (d) Photos showing the elasticity of knitted fabrics [36]. Cao et al. (2022), Elsevier. (e) Schematic representation of TENG composed of Al and PTFE modified by ion implantation. (f) The left half is the schematic diagram of the equipment. The right half is the real device image based on the left, and 20 LED lights can light up in series [39]. Fan et al. (2021), Elsevier. (g) The schematic outline of the charge-catching system of 3L-Gr-TENG shows the case without and with the Al2O3 charge-catching layer [40]. Sahoo et al. (2021), MDPI. (h) (I) The finished product photo (II) two different deformation states of the OSHD-TENG. (III) LM electrode conductivity test photo [41]. Zhong et al. (2022), Elsevier.