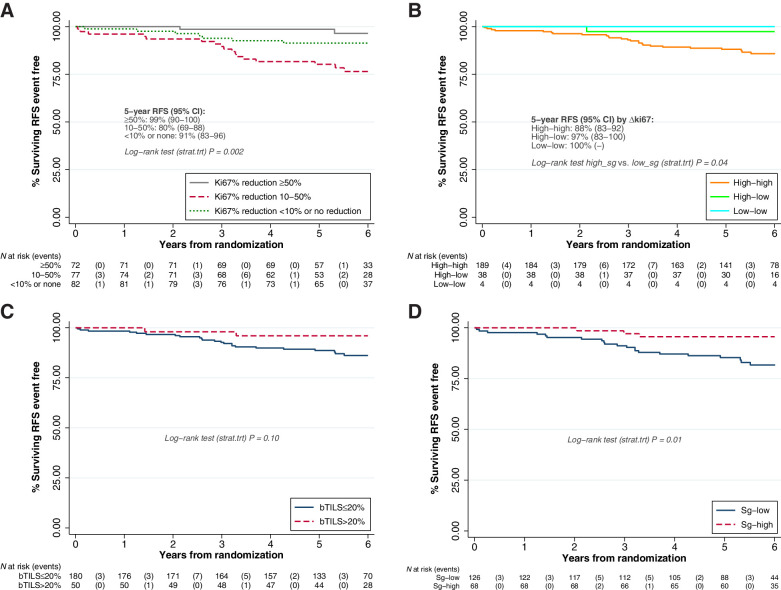
Figure 3.
Association of perioperative changes in biological markers with RFS (A) by categories of Ki67 relative change, (B) by categories of Ki67 absolute change, (C) by baseline TILs, (D) by surgery TILs. RFS is represented in the time interval 0 to 6 years, as no RFS events occurred beyond 6 years from randomization. All treatment groups are combined; log-rank tests are stratified by treatment group (P = P value). For A and B, a value of −100% Ki67 change (ΔKi67) has been imputed for patients with a pCR in breast. For B, we have categorized both baseline and surgery Ki67 into high if ≥10% or low if <10%. No patient increased Ki67 from low to high after 11 days of perioperative treatment. Because of small number of patients in the “low–low” group, we have compared patients with “high” value at surgery with patients with “low” value at surgery.