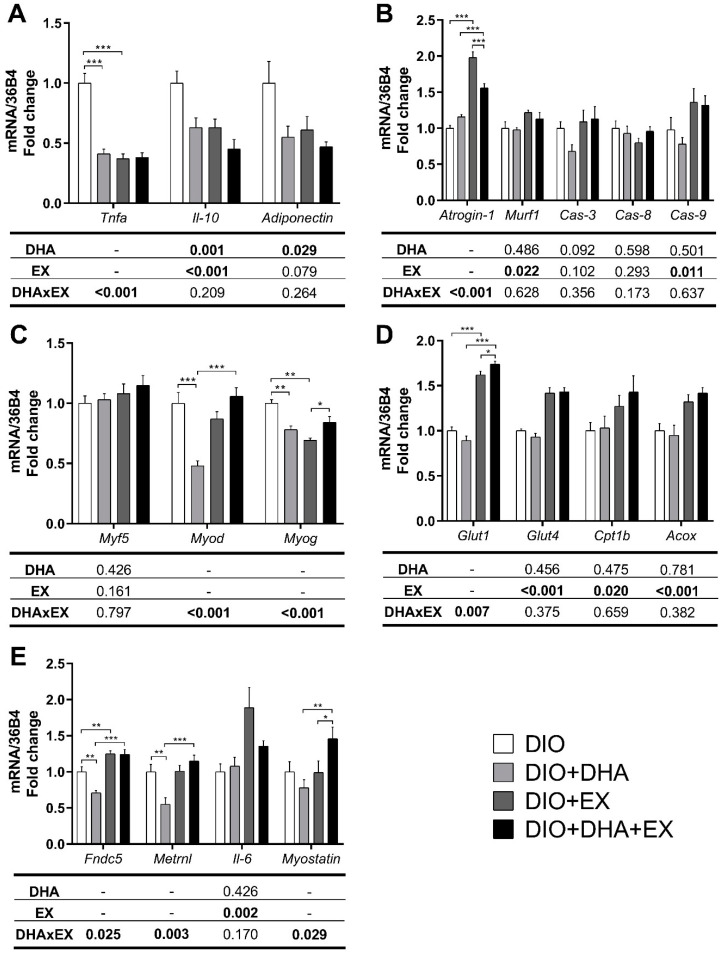
Figure 3.
Effects of long-term DHA supplementation and/or exercise training on genes related to inflammation (A), muscle damage (B), muscle regeneration (C), glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation (D) and myokine expression (E) in the gastrocnemius muscle of 18-month-old DIO female mice. Data presented as mean (SD); n = 6–10. DIO: Diet-induced obese; EX: Treadmill training. For two-way ANOVA, when an interaction was found, contrast analysis was performed. The p values for the main factors, DHA supplementation (DHA), exercise (EX) and the interaction between both (DHAxEX) are shown in the corresponding rows of the tables below the figures. Statistically significant p values are marked in bold. Significant differences between groups are shown above the corresponding comparisons: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.