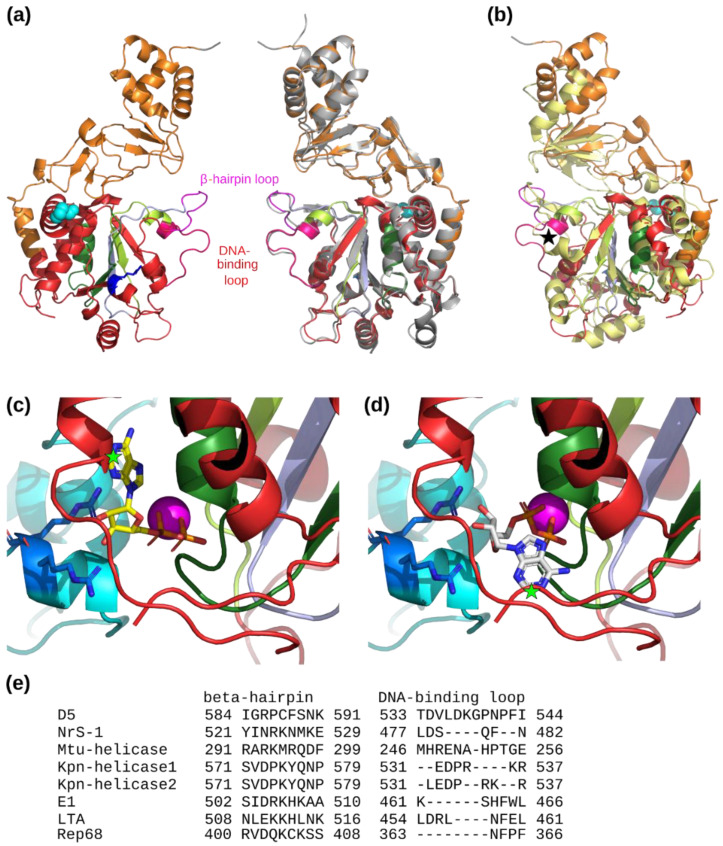
Figure 7.
Analysis of the AAA+ helicase and collar domains. (a) Two opposite subunits of the refined structure are shown with the AAA+ helicase motifs in color: Walker A, dark green; Walker B, light green; Motif C, light blue; Arg-finger, blue. The residue Pro682 leading to a temperature-sensitive mutant is shown with cyan spheres. The loops corresponding to interactions with DNA in the translocation mechanism are colored in magenta (β-hairpin loop) and bright red (DNA-binding loop). Right subunit: structure from the Alphafold2 prediction (gray) compared to the refined C6 structure. (b) Superposition of the NrS-1 AAA+ helicase domain (bright yellow) on the corresponding domain of D5 colored as in panel (a). A black star indicates the much shorter DNA-binding loop in NrS-1 helicase. (c) View of the cartoon structure around the nucleotide binding site at the subunit interface of D5323–785 with the ADP and Mg2+ ion positions inferred from papillomavirus E1 (pdb entry 2gxa, chain A). The superposition of the two structures used the AAA+ helicase motif from Iyer and coworkers [12] colored as in panel (a). The neighboring chain contributing the arginine finger (blue sticks) is colored in cyan. The predicted clash of the base with the helicase structure is indicated by a green star. (d) Same view of D5323–785 with ADP and Mg2+ ion positions inferred from polyoma virus LTA (pdb entry 1svl, chain A). (e) Sequence alignment of the residues forming the β-hairpin and DNA-binding loops of SF3 helicases mentioned in the text where experimental or predicted structural information is available.