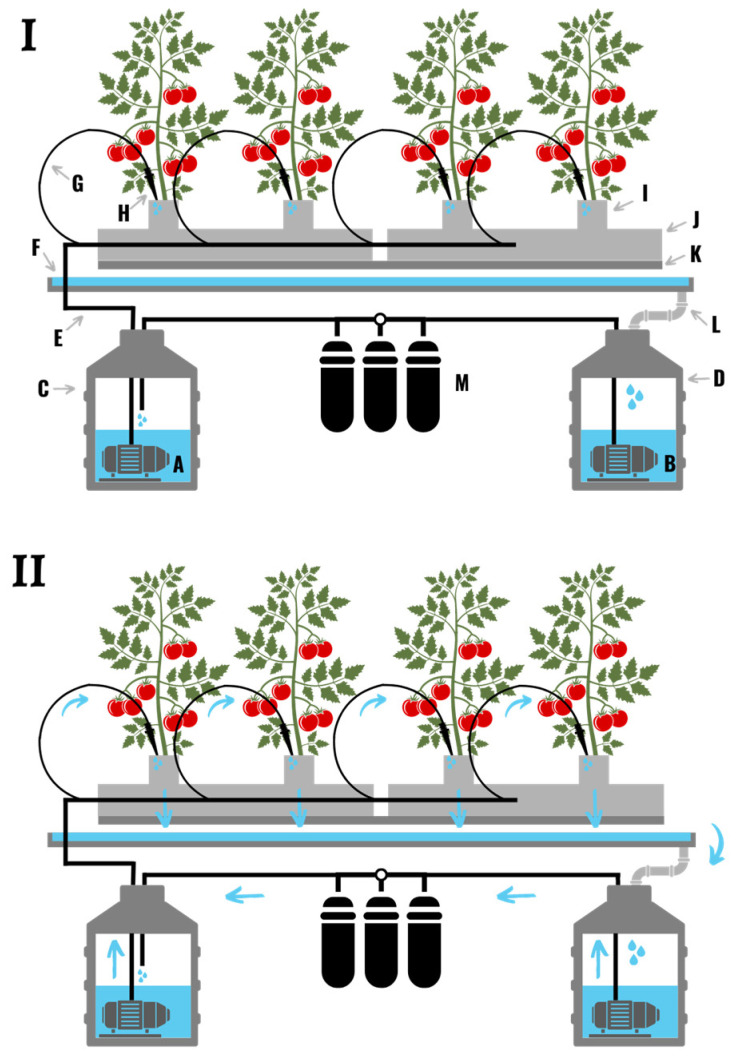
Figure 4.
(I) A drip irrigation system comprised of water pumps (A,B), two reservoirs (C,D), a watering line/pipe (E), a drain trough (F), drip lines (G), drip stakes (H), a smaller grow media cube than the transplanted plant was propagated in (I), a large grow media slab (J), a platform (K), a drainpipe (L), and a water purification system (M). (II) Several times a day water is pumped from the storage reservoir, through the drip lines and over the roots of the plants. The nutrient solution that runs off the roots of the plant is usually filtered and sterilized to eliminate any pathogens prior to recirculation. The nutrients content of the collected nutrient solution is then adjusted back to desired levels before it is recirculated back onto the plants. In non-recirculated systems water is collected in a drainage trough and fed back to a central reservoir. The nutrient solution is then filtered and sterilized to remove particulates and pathogens.