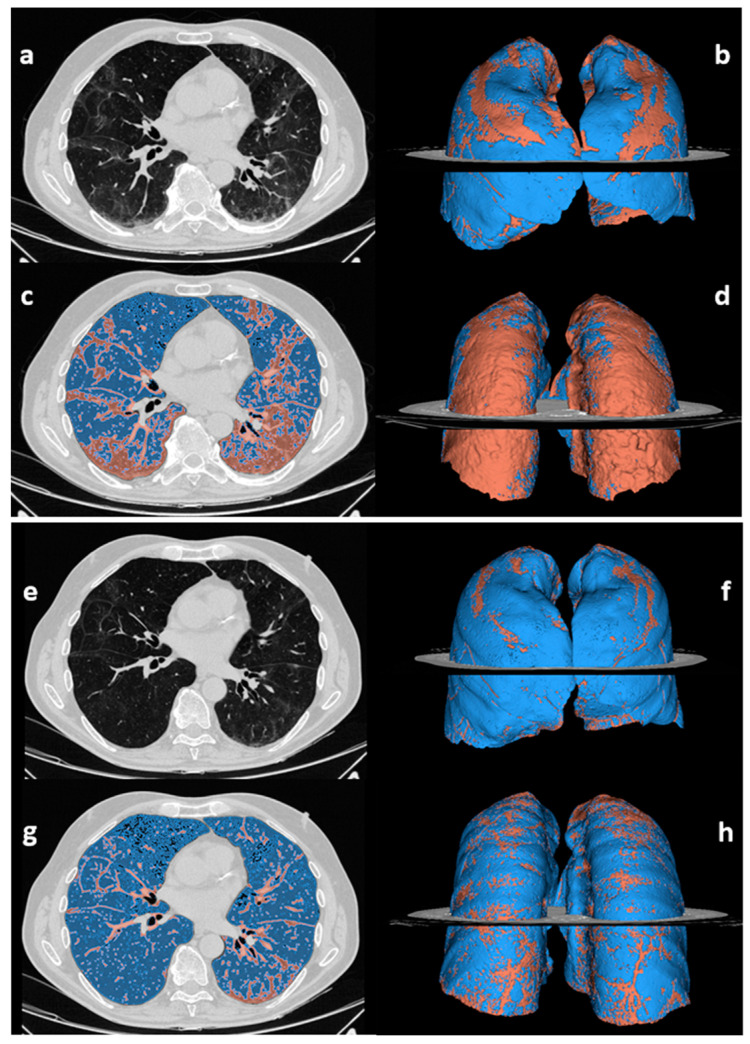
Figure 2.
Abnormal lung volume quantification on chest CT scans acquired at 3 months (a–d) and 12 months after discharge (e–h) in a 70-year-old male patient who suffered from severe COVID-19. The unenhanced chest CT scans (a,e) are displayed alongside the pertinent segmentations of residual lung abnormalities (red) and normally aerated lung (blue) performed by 3D Slicer software (c,g), and the related 3D anterior (b,f) and posterior (d,h) volumetric representations. The case is representative of the subgroup of patients with improved but still abnormal chest CT findings (group 3). The percentage of abnormal lung volume decreased over time, from 33% at three months (b,d) to 13% at 12 months after discharge (f,h). The dorsal segments are the most impacted by residual CT findings at 12 months.