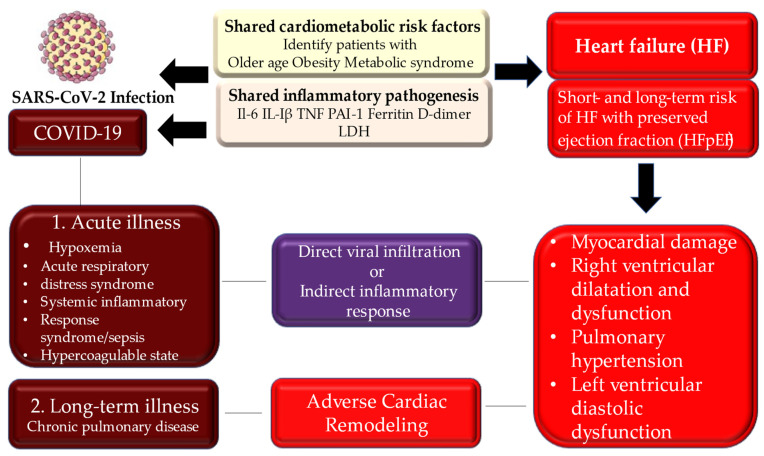
Figure 4.
Depicts the potential intersection of acute and chronic phases of COVID-19 and risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Population at higher risk of infection and development of disease may experience an acute illness or progression toward a long-term illness. Direct viral infiltration or indirect inflammatory response, as well as adverse cardiac remodelling, can lead to chronic heart and pulmonary disease. Abbreviations: COVID-19 indicates coronavirus disease 2019; IL: interleukine; HF, heart failure; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.