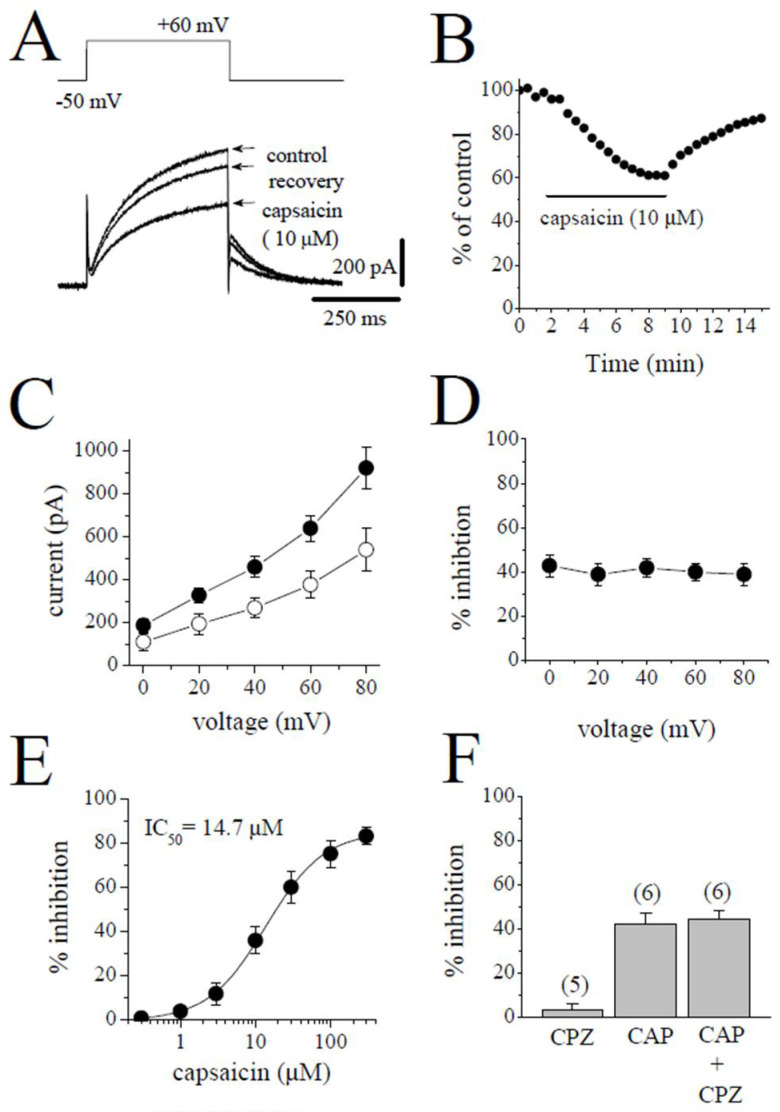
Figure 4.
Capsaicin suppresses the IKs component of the delayed rectifying IK. (A) Superimposed current traces in control, after 8 min exposure to 10 μM capsaicin, and recovery. The pulse protocol to activate IKs is shown as an inset. (B) Time course of the effect of capsaicin effect on the maximal amplitudes of IKs and washout presented as % of control calculated from the mean of three control currents. (C) Current–voltage relationships of IKs in the absence and presence of 10 μM capsaicin are presented with filled and open circles, respectively (n = 5). (D) The relationship between test potential and the capsaicin (10 µM) inhibition of IKs (n = 5; p > 0.05, ANOVA). (E) Concentration-inhibition curve for capsaicin inhibition of IKs (n = 4–6). (F) The effect of capsazepine (3 µM) and the extent of capsaicin (10 µM) inhibition of IKs in the absence and presence of 3 µM capsazepine. The number of cells tested for each group was presented on top of each bar (p > 0.05; t-test).