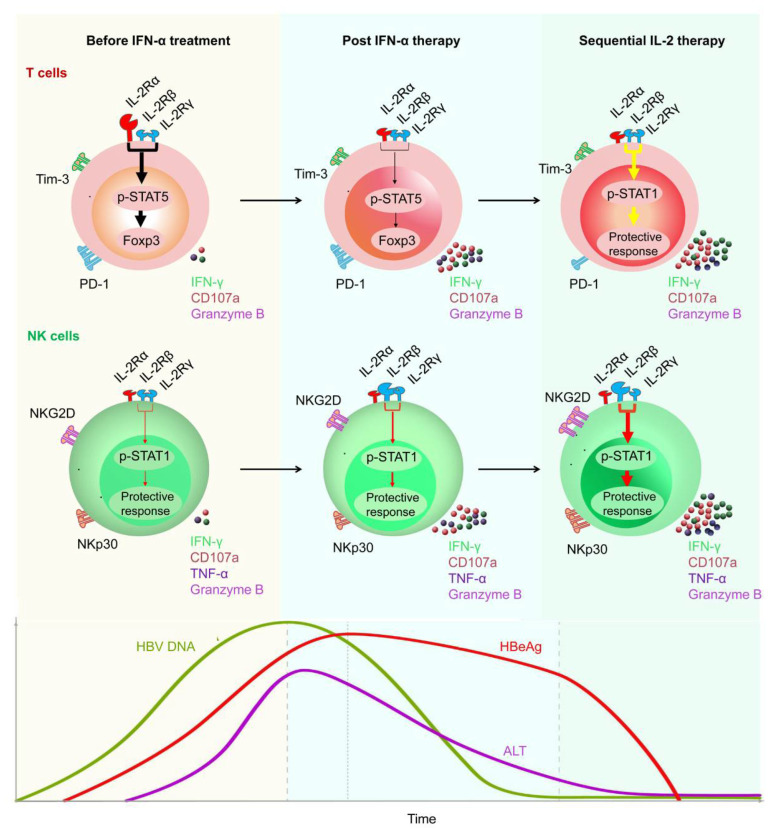
Figure 3.
Restoration of HBV-specific CD8+ T cell and NK cell responses by sequential IL-2 treatment in non-responder patients after IFN-α therapy. IL-2Rα was high expressed, and NKp30 was low expressed on T cells and NK cells, respectively, of non-responder (NR) patients, in whom IFN-α therapy had failed. Those NR patients were treated with low-dose IL-2 for 24 weeks. A decrease in IL-2Rα expression on their CD4+ T cells was verified, suggesting that IFN-α therapy may provide a rationale for sequential IL-2 treatment without increasing regulatory T cells (Tregs). In addition, non-responders experienced a decrease in the numbers of PD-1 expression. Furthermore, sequential IL-2 administration restored effective immune function, involving STAT1 activation in both T cells and NK cells. Moreover, IL-2 therapy increased the function of HBV-specific T cells and NK cells, which translated into improved clinical outcomes, including HBeAg seroconversion, among the non-responder CHB patients.