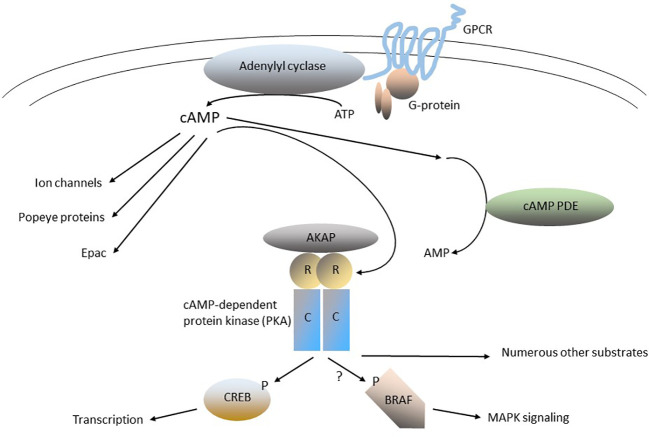
Figure 1.
The cAMP-signaling pathway. G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of 7-helix transmembrane proteins that are the physiological receptors for circulating hormones (e.g., TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH, among many others) and neurotransmitters that bind to their extracellular regions (the plasma membrane is indicated by the pair of curved lines). Orphan GPCRs (e.g., that encoded by GPR101), encode GPCRs for which the physiologic ligand has yet to be determined. GPCRs interact with trimeric G-proteins by recruiting them to specific regions on their intracellular loops. G-proteins have three subunits (α, β, or γ) and the members of the α family can be divided into stimulatory (Gαs) or inhibitory (Gαi) isoforms (e.g., GNAS is one of several genes encoding Gαs isoforms). Gα and/or Gβγ bind to, and regulate, one of several downstream effectors, including membrane-associated adenylyl cyclase, which catalyzes the synthesis of cAMP from ATP. cAMP is a soluble “second messenger” that can diffuse widely in cells. cAMP phosphodiesterases (PDEs) catalyze the hydrolysis (breakdown) of cAMP and thereby play a central in regulating cAMP signaling in cells. cAMP can activate several targets, including the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A, PKA), EPAC, Popeye proteins and ion channels. The PKA holoenzyme is a tetramer of 2 catalytic subunits (C-subunits, Cα or Cβ), and 2 regulatory subunits (R-subunits, RIα, RIβ RIIα or RIIβ). The subcellular localization of PKA is determined by its binding to A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). In the inactive PKA holoenzyme, the R-subunits bind tightly to the C-subunits and inhibit their activity. cAMP activates PKA by binding to the R-domains, producing a conformational change that activates the C-domains. PKA is a serine-threonine protein kinase that can phosphorylate numerous substrates, depending on the specific cell type and subcellular location. The cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) is an important substrate and downstream target of PKA; it regulates the transcription of numerous genes. The oncoprotein BRAF is regulated in part by PKA, as well as other signaling proteins, such as RAS proteins and tyrosine-protein kinases.