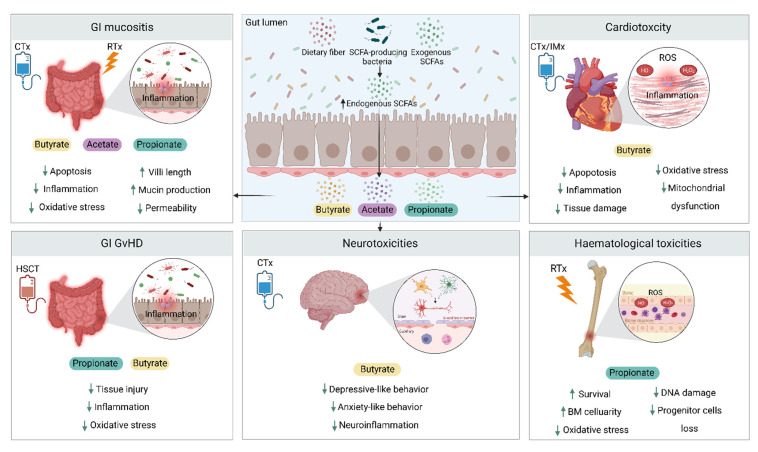
Figure 3.
The role of SCFAs in cancer treatment toxicities based on current evidence. SCFAs can alleviate chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and HSCT-induced GI damage associated with mucositis and GvHD by reducing cell death, inflammatory and oxidative stress responses, and decreasing intestinal permeability by protecting villi length and enhancing mucin production. Butyrate protects against chemotherapy-related cardiac toxicities by reducing tissue injury, inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Butyrate also has beneficial effects against chemotherapy-induced behavioral changes and neuroinflammation. Propionate protects against hematological toxicities by enhancing bone marrow cellularity and reducing DNA damage, oxidative stress, and progenitor cell death. SCFAs, short chain fatty acids; GI, gastrointestinal; CTx, chemotherapy; RTx, radiotherapy; IMx, immunotherapy; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GvHD, graft-versus-host disease; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.