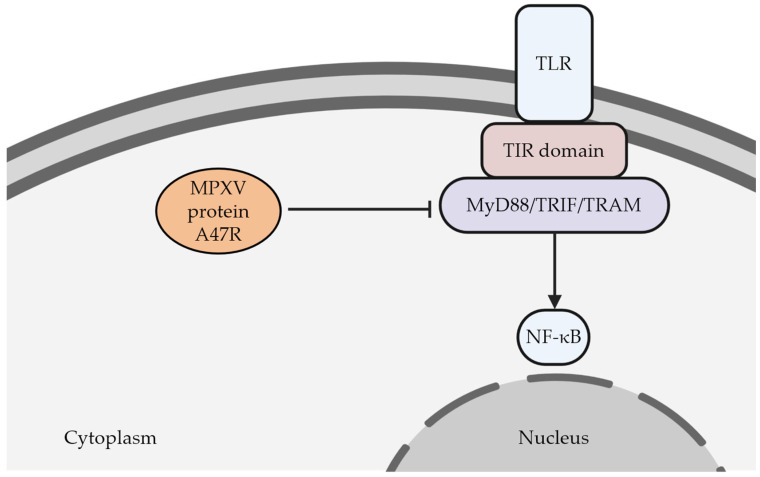
Figure 4.
As a member of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), TLR plays a critical role in recognizing various noxious molecules. Upon its interaction with those molecules, the cytoplasmic domain (TIR) of TLR recruits the appropriate adaptor proteins (e.g., MyD88, TRIF, or TRAM). This interaction induces the subsequent molecular pathways that will eventually upregulate the expression of NF-κB, which is critical in modulating the innate immune system. It has been found that this mechanism can be impaired by the action of a MPXV protein called A47R. This viral protein can interact with the adaptor proteins leading to the impairment of viral recognition by the immune system. TLR (Toll-like receptor); TIR (Toll/interleukin-1 receptor); MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary-response gene 88); TRIF (TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFNβ); TRAM (TRIF-related adaptor molecule); NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B). The figure was created by Biorender.