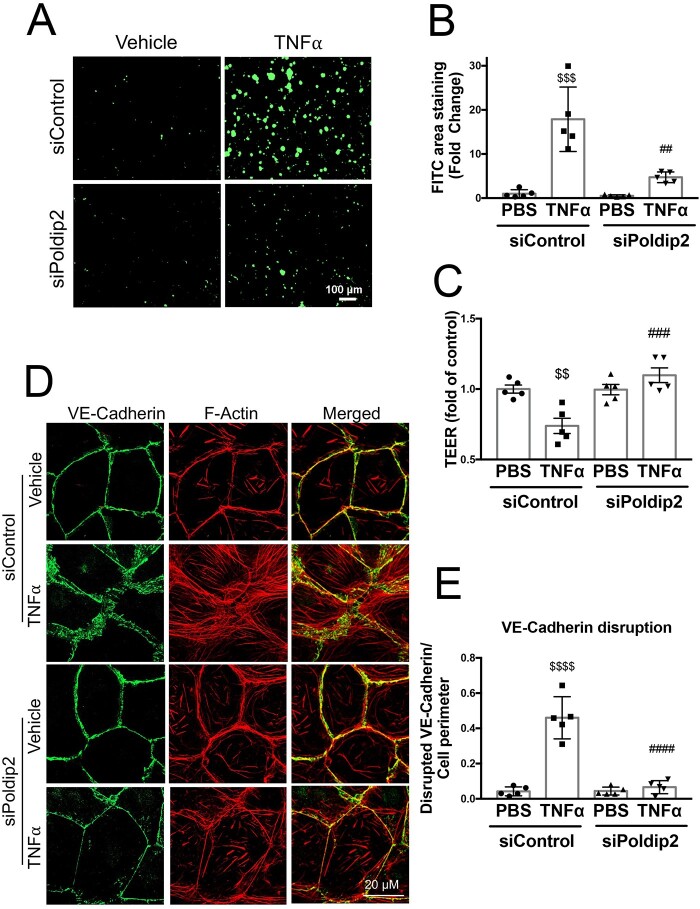
Figure 4.
Poldip2 knock-down reduces endothelial permeability and preserves junctional organization in response to inflammation. (A) TNFα treatment induced intercellular gap formation in HLMECs, as assessed by the increased binding of FITC-avidin to collagen-biotin coated dishes. Poldip2 knock-down diminished gap formation in response to TNFα. Images quantified in (B) represent averages ± SEM (n = 5). $$$P < 0.001 compared to siControl PBS, ##P < 0.01 compared to siControl TNFα (two-way ANOVA, with Tukey’s correction). (C) TEER results showing significant decrease in endothelial resistance in siControl treated cells after TNFα treatment compared to siControl and PBS-treated cells. This decrease was not observed in siPoldip2 treated cells (n = 5), $$P < 0.01 compared to PBS siControl treated cells, ###P < 0.001 compared to TNFα and siControl treated cells (two-way ANOVA, with Tukey’s correction). TNFα induced disruption of VE-cadherin at the cell–cell junction along with actin disorganization and stress-fibre formation in HLMECs, while knocking down Poldip2 prevented these effects (D). Images quantified in (E) represent averages ± SEM (n = 5). P < 0.0001 compared to PBS siControl treated cells, ####P < 0.0001 compared to TNFα siControl treated cell (two-way ANOVA, with Tukey’s correction).