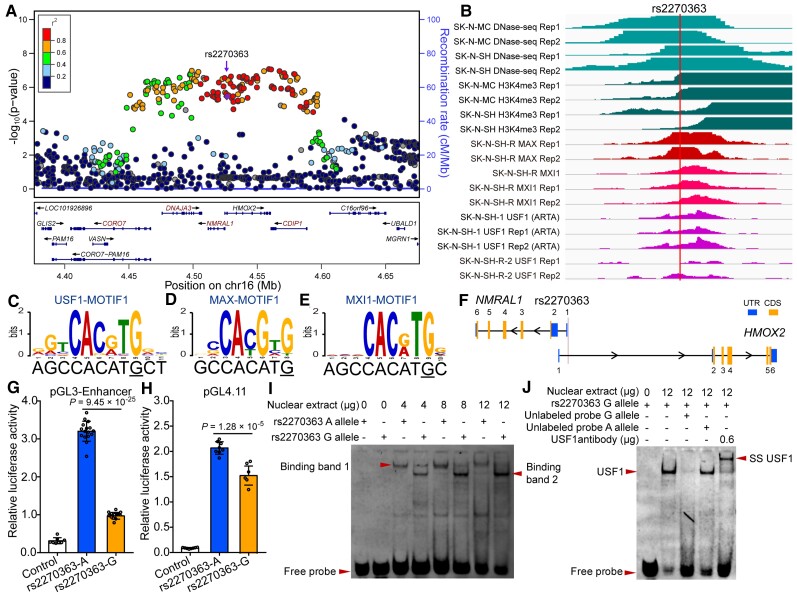
Figure 1.
Validation of regulatory effects of rs2270363 at the 16p13.3 risk locus. (A) The Locus zoom plot showed the associations between variants in genomic region (300 kb) containing rs2270363 and schizophrenia in the PGC2 + CLOZUK study. (B) ChIP-Seq data showed that transcription factors USF1, MAX and MXI1 could bind to genomic sequence containing rs2270363 (data from ENCODE). (C–E) rs2270363 disrupts binding motif (i.e. position weight matrix, PWM) of USF1, MAX and MXI1. (F) SNP rs2270363 is located in the promoter of NMRAL1 gene. (G and H) Dual-luciferase reporter gene assays showed that rs2270363 affected promoter activity in SH-SY5Y cells regardless of its orientation. The vector containing A allele of rs2270363 exhibited significant higher luciferase activity compared with G allele. (I) EMSA showed that rs2270363 affected binding of transcription factors. One binding band (band 1, marked with arrowhead) was detected for the A allele, while two binding bands (band 1 and 2) were detected for the G allele. (J) Super-shift and competitive experiments for EMSA. Super-shift assay showed that rs2270363 binds to USF1 (the super-shift band was detected in the lane with added USF1 antibody) and competitive experiments revealed that the G allele had stronger binding affinity compared with the A allele. n = 8 for control group in G, n = 16 for experimental group in G, n = 8 for H. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to test if the difference reached significance level (P = 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SD.