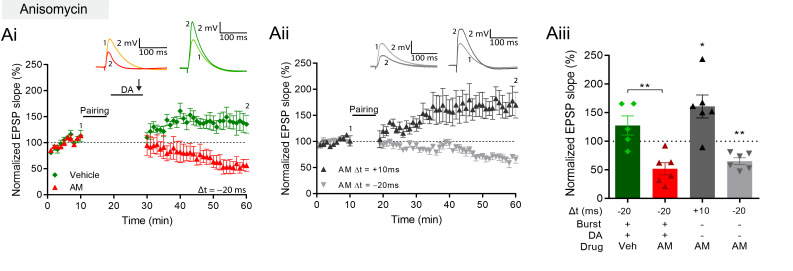
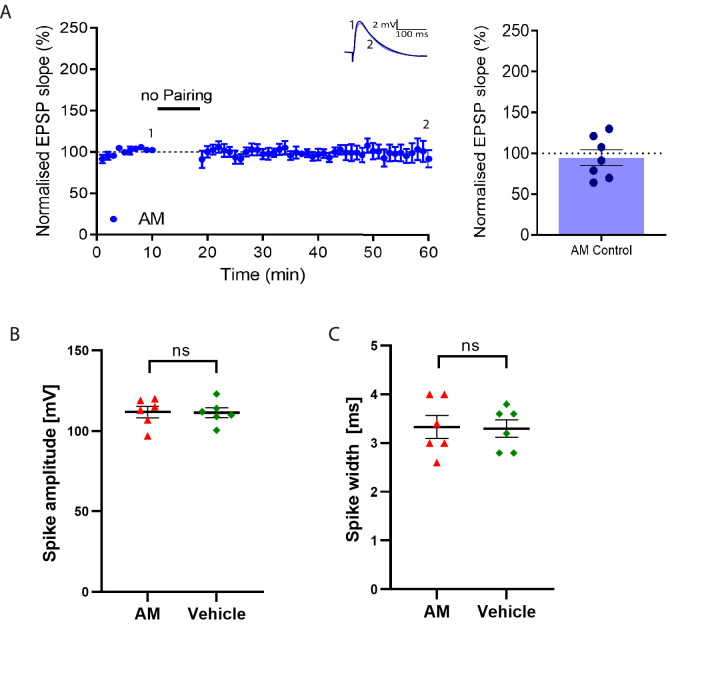
Figure 5. DA and reactivation-induced plasticity requires protein synthesis.
(A), Postsynaptic anisomycin prevents DA-dependent plasticity with postsynaptic burst stimulation (Ai), but leaves conventional t-LTD (Aii, gray trace) and t-LTP (black trace) intact. Summary of results (Aiii). All traces show an EPSP before (1) and 40 min after (2) pairing. Plots show averages of normalized EPSP slopes ± SEM.