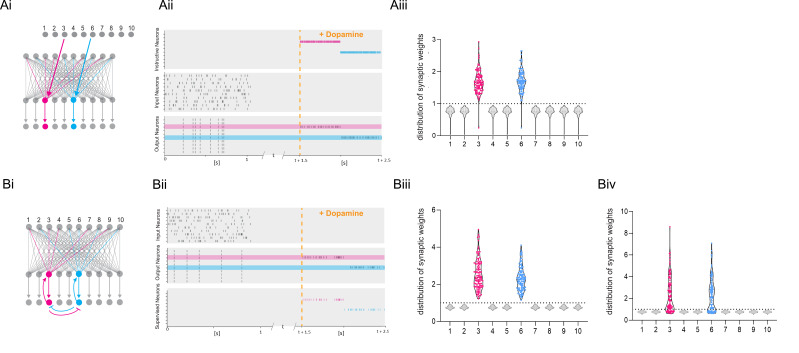
Figure 7. Dopamine-dependent burst-induced plasticity rule enables reinforcement learning (RL) models to encode a specific salient event.
(Ai-iii), Instructive RL rule allows two inputs that code for different information to store the memory in separate sets of neurons, thus encoding not only the reward, but also other reward-relevant features 3, 6 (magenta, cyan). (Bi-ii), A supervised network enables burst-eliciting feedback synaptic input to assign credit to select synapses in the network to encode a desired reward identity. (Biii) Time-dependent lateral inhibition at the output neurons suppress non-relevant information. When only one of the inputs is active, the animal can learn two different memories over time in neurons 3, 6 (magenta, cyan). (Biv) When both inputs are active at the same time they compete with each other, and synapses onto these neurons (magenta, cyan) are less potentiated.