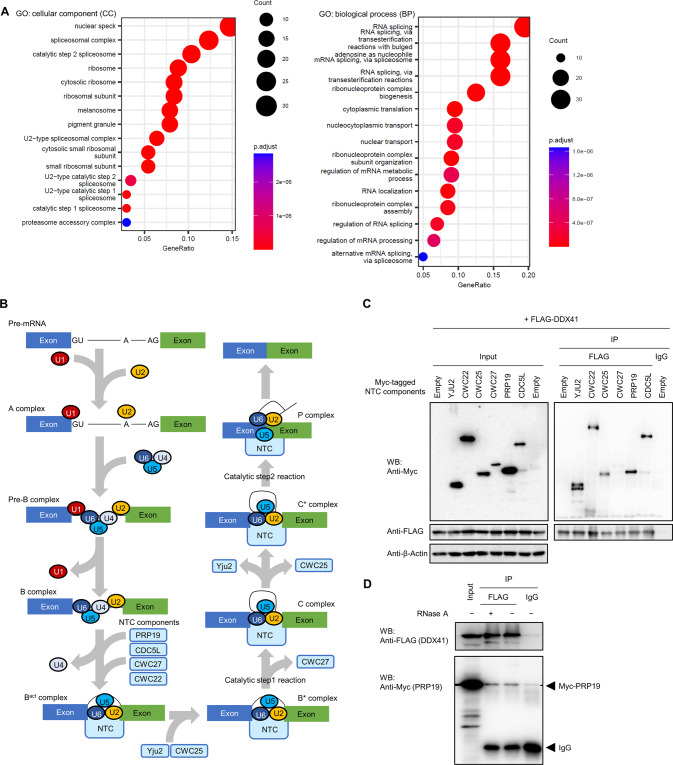
Fig. 2. Interaction of DDX41 with RNA splicing-related proteins.
A Major GOs of proteins interacted with FLAG-DDX41. Nuclear proteins immunoprecipitated with FLAG-DDX41 were categorized via GO analysis. Top 15 GO terms for CC (cellular component) and BP (biological process) categories are shown, with the number of genes indicated by circle sizes and adjusted p values indicated by red to blue colors. B Schematic diagram showing NTC involvement in RNA splicing. The factors within NTC are incorporated into or excluded from the complex depending on the splicing steps, in which core NTC components (PRP19 and CDC5L) occur throughout NTC after incorporation of the complex into the spliceosome; CWC25 and Yju2 are incorporated before the B* complex and excluded before the C* complex, and CWC27 is excluded before the C complex. C Interaction of DDX41 with RNA splicing process-specific components in the NTC. Myc-tagged NTC components (Yju2, CWC22, CWC25, CWC27, PRP19, and CDC5L) were expressed with FLAG-tagged DDX41 in HEK293FT cells, and DDX41-interacting proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. Precipitated proteins were probed with anti-FLAG, anti-Myc, or anti-β-Actin antibody. Left and right panels indicate input and immunoprecipitated samples, respectively. D Non-RNA-mediated interaction of DDX41 with PRP19. FLAG-tagged DDX41 and Myc-tagged PRP19 were expressed in HEK293FT cells, and FLAG-DDX41 was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. Precipitated samples were then treated with 20 μg/ml RNase A for 30 min at 37 °C before being probed with anti-FLAG or anti-Myc antibody.