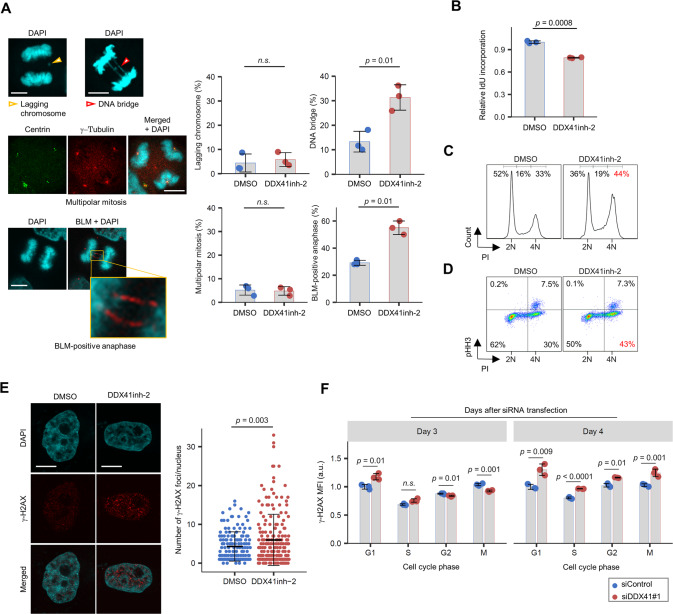
Fig. 5. Mild replication stress by DDX41 inhibition triggers mitotic abnormalities and affects cell cycle progression of daughter cells.
A Increased DNA bridges and ultrafine DNA bridges in mitotic HeLa cells treated with DDX41inh-2 during S phase. See Supplementary Fig. S5A for schematic. (Left) Representative images of abnormal mitosis. (Right) Quantitative result of abnormal mitosis. Bars indicate means; error bars, SD of triplicate samples; two-tailed Welch’s t test. n.s., not significant. Scale bars: 10 μm. B Reduced IdU incorporation in cells that had been treated with DDX41inh-2 in S phase and had undergone mitosis. See Supplementary Fig. S5A for schematic. Bars indicate means; error bars, SD of triplicate samples; two-tailed Welch’s t test. C, D Cell cycle arrest at G2 phase in HeLa cells that had been treated with DDX41inh-2 in S phase and had undergone mitosis. Cells were treated as in Fig. 4I. Cell cycle status 18 h after removal of DDX41inh-2 and RO-3306 was identified by PI staining (C). Cells were double-stained with PI and anti-pHH3 antibody to distinguish mitotic cells from cells at G2 (D). E Increase in γ-H2AX foci in G1 HeLa cells that had been treated with DDX41inh-2 in S phase and had undergone mitosis. Cells were stained with anti-γ-H2AX antibody and DAPI. See Supplementary Fig. S5B for schematic. Bars represent means ± SD; n = 151 and 195 for DMSO and DDX41inh-2, respectively; two-tailed Welch’s t test. Scale bars: 10 μm. F Increase in γ-H2AX signals primarily occurred at G1 in HeLa cells after DDX41 knockdown. Cells were stained with anti-γ-H2AX and anti-pHH3 antibodies and PI. MFI of γ-H2AX in each cell cycle phase was analyzed with flow cytometry. Bars indicate means; error bars, SD of triplicate samples; two-tailed Student’s t test.