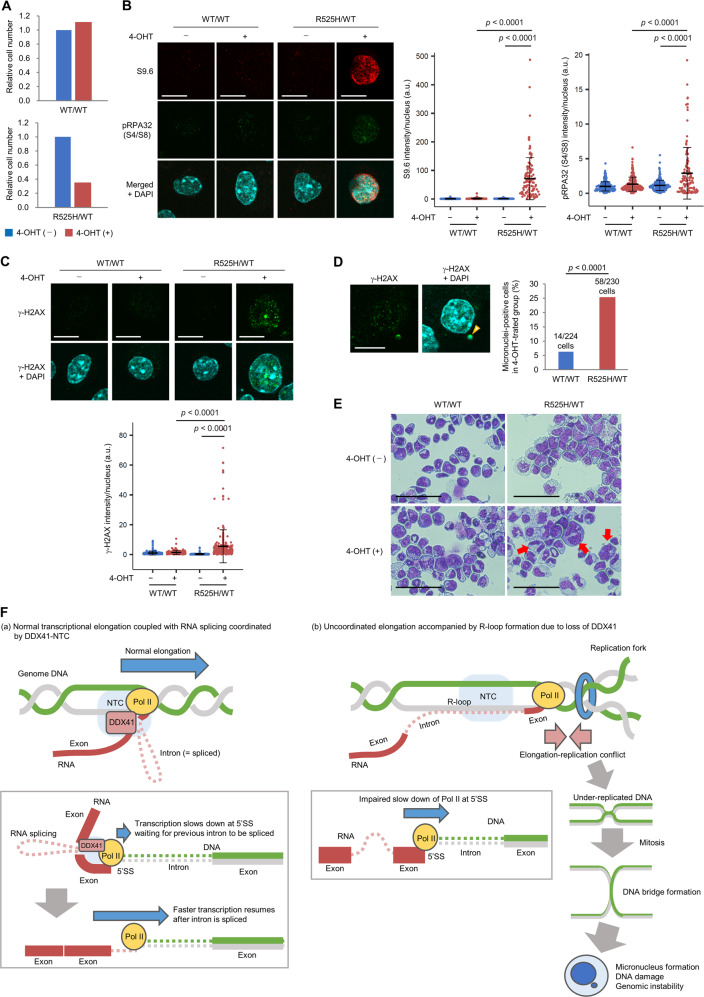
Fig. 8. R-loop accumulation and DNA damage by introduction of R525H mutation in primary hematopoietic progenitor cells in mice.
A Reduced proliferation of immature bone marrow cells expressing R525H mutation. Lin−/c-Kit+ bone marrow cells isolated from 9-week-old Ddx41R525H/WT or Ddx41WT/WT mice were cultured ex vivo in the presence of 25 ng/ml human thrombopoietin (TPO), 50 ng/ml mouse stem cell factor (SCF), 50 ng/ml mouse FLT3-L, and 25 mg/ml mouse interleukin-6 (IL-6) for 72 h, and then 4-OHT at 200 nM (final concentration) was added to culture medium for 48 h. Relative cell numbers compared with control cell numbers cultured in the presence or absence of 4-OHT are shown. B, C Increased R-loop formation and DNA damage in immature bone marrow cells expressing Ddx41 R525H mutation. Cells cultured as in A were stained with S9.6 and anti-phospho-RPA32 (S4/S8) antibodies (B) or anti-γ-H2AX antibody (C) with nuclear DAPI counterstaining. Scale bars: 10 μm. (Right) Quantitative signal levels. n = 246, 217, 226 and 128 (B), and 238, 151, 190, and 290 (C) for WT/WT/4-OHT−, WT/WT/4-OHT+, R525H/WT/4-OHT−, and R525H/WT/4-OHT+, respectively; two-tailed Welch’s t test. D Micronucleus formation in immature bone marrow cells expressing Ddx41 R525H mutation. Cells cultured as in A were stained with DAPI and anti-γ-H2AX antibody. (Left) Representative images of Ddx41R525H/WT cell with γ-H2AX-positive micronucleus (arrowhead). Scale bar: 10 μm. (Right) Percent micronuclei-positive cells. Chi-square analysis. E Morphology of hematopoietic progenitor cells cultured ex vivo. Cells cultured as in A were stained with Giemsa and observed with light microscopy at ×400. Red arrows indicate cells with severely abnormal nuclear morphology. Scale bars: 50 μm. F Schematic illustration of how DDX41 deficiency causes impaired hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. (a) Normal condition: DDX41, together with NTC, coordinates RNA splicing and transcriptional elongation. The Pol II complex transiently slows at 5ʹSS by interacting with DDX41, where it waits until the intron is spliced. (b) DDX41 deficiency: Pol II complex ignores unfinished RNA splicing and does not slow at 5ʹSS, which leads to increased opportunities for R-loop formation and transcription-replication conflicts. This results in increased under-replicated DNA at end of replication and DNA bridge formation during mitosis that result in genomic instability.