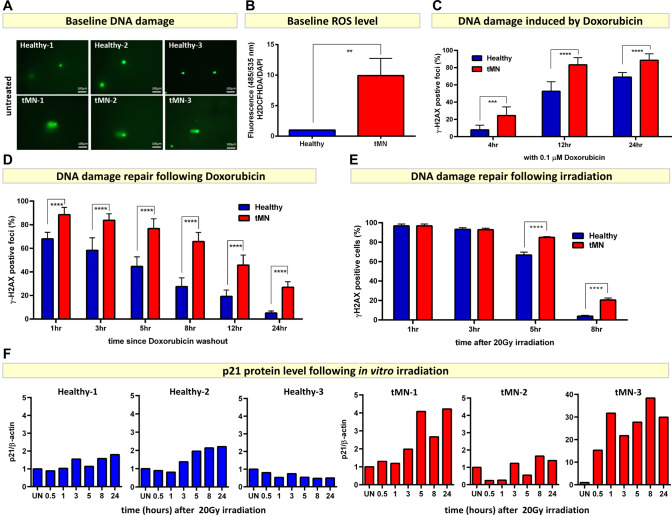
Fig. 3. tMN stromal cells exhibit defective DNA damage repair potential.
A Alkaline comet assay shows high level of baseline DNA damage in tMN (n = 3) compared to Healthy (n = 3) BMSC. The length of the comet tail reflects the number of DNA breaks; B high level of baseline DNA damage is probably driven by high level of ROS in tMN compared to Healthy BMSC; C significantly high number of γH2AX foci formation were evident after 4, 12, and 24 h of exposure to 0.1 µM Doxorubicin, a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug; D defective DNA damage repair potential of tMN BMSC was evident by significantly high number of γH2AX foci at all time points following Doxorubicin drug-washout; E following in vitro radiation, number of γH2AX foci in Healthy BMSC decreased with only 4 ± 1% cells showing positivity by 8 h after irradiation. However, tMN BMSC showed significantly impaired repair with 21 ± 2% foci still positive at the same time point; F densitometry analysis of Western blots showing p21 protein expression normalized to β-actin in three tMN and Healthy BMSC analyzed. UN, untreated. All bars indicate mean, and all error bars indicate SD. Mann–Whitney test was used to detect statistically significant differences between two groups and Two-way ANOVA was used to determine differences among groups. Asterisks display P values **P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001.