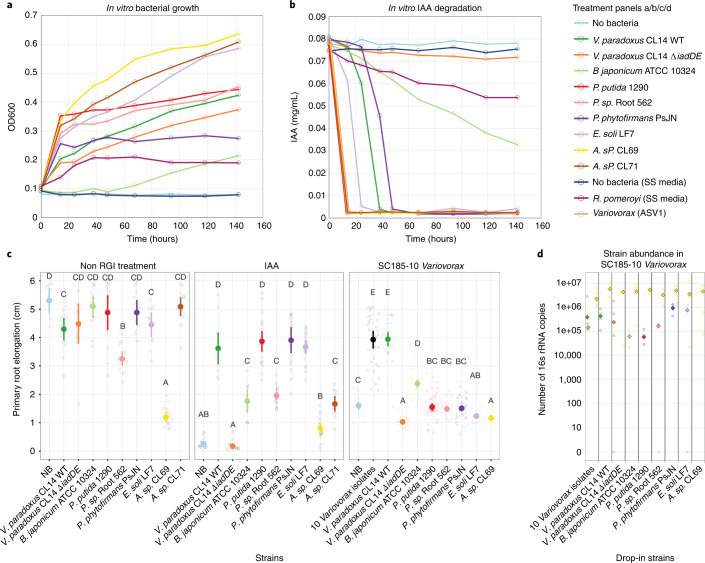
Fig. 6. Strains encoding iad-like IAA degradation loci perform the metabolic signal interference required to prevent RGI caused by a 175-member synthetic microbiome community on Arabidopsis roots.
a,b, Growth as measured by OD600 (a) (n = 3) and IAA degradation by diverse IAA-degrading strains in M9 medium with amino acids and IAA (b) (n = 3). R. pomeroyi was grown in identical medium supplemented with 2% (w/v) sea salts (SS media). c, Measurement of primary root elongation confirms that IAA-degrading strains can prevent IAA-induced RGI, but only representatives from Variovorax and Bradyrhizobium (both carrying iad-like loci) are able to prevent RGI induced by a 175-member synthetic community (SC185-10V, a 185-member synthetic community used previously14 minus its 10 Variovorax members). Mean primary root elongation is shown as a bold circle with 95% confidence interval. Significance was determined via the fitting of an ANOVA model within each panel with the design primary root elongation ~ Bacteria; letters above each treatment represent the compact letter of a Tukey post hoc test. Left to right: no RGI treatment: n = 53, 18, 17, 17, 24, 15, 15, 12 and 15, 19 biological replicates; IAA: n = 19, 13, 20, 11, 22, 20, 17, 20, 20 and13 biological replicates; SC185-10V: n = 41, 36, 33, 40, 44, 45, 39, 50, 39 and 44 biological replicates over 2 independent experiments. d, 16S absolute abundance measurement (n = 5 open circles, median shown as diamond with black contour) confirms colonization and persistence of all IAA-degrading strains in the SC185 minus 10 Variovorax synthetic community even for the iac-like loci-containing bacteria that do not revert the RGI phenotype in Arabidopsis roots shown in c. Variovorax ASV1 (grey) corresponds to Variovorax 16S amplicon sequence variants of Variovorax strains in the ‘10 Variovorax isolate’ treatment that are distinct from the Variovorax CL14 ASV (dark green). Acinetobacter sp. CL69 is present in SC185-10V and is thus found in all samples. Each panel in the figure focuses on a specific drop-in treatment, with the respective inoculated strains highlighted on the x axis.