Figure 2. Patients with the hyperfibrinolysis phenotype produce abnormal fibrin networks.
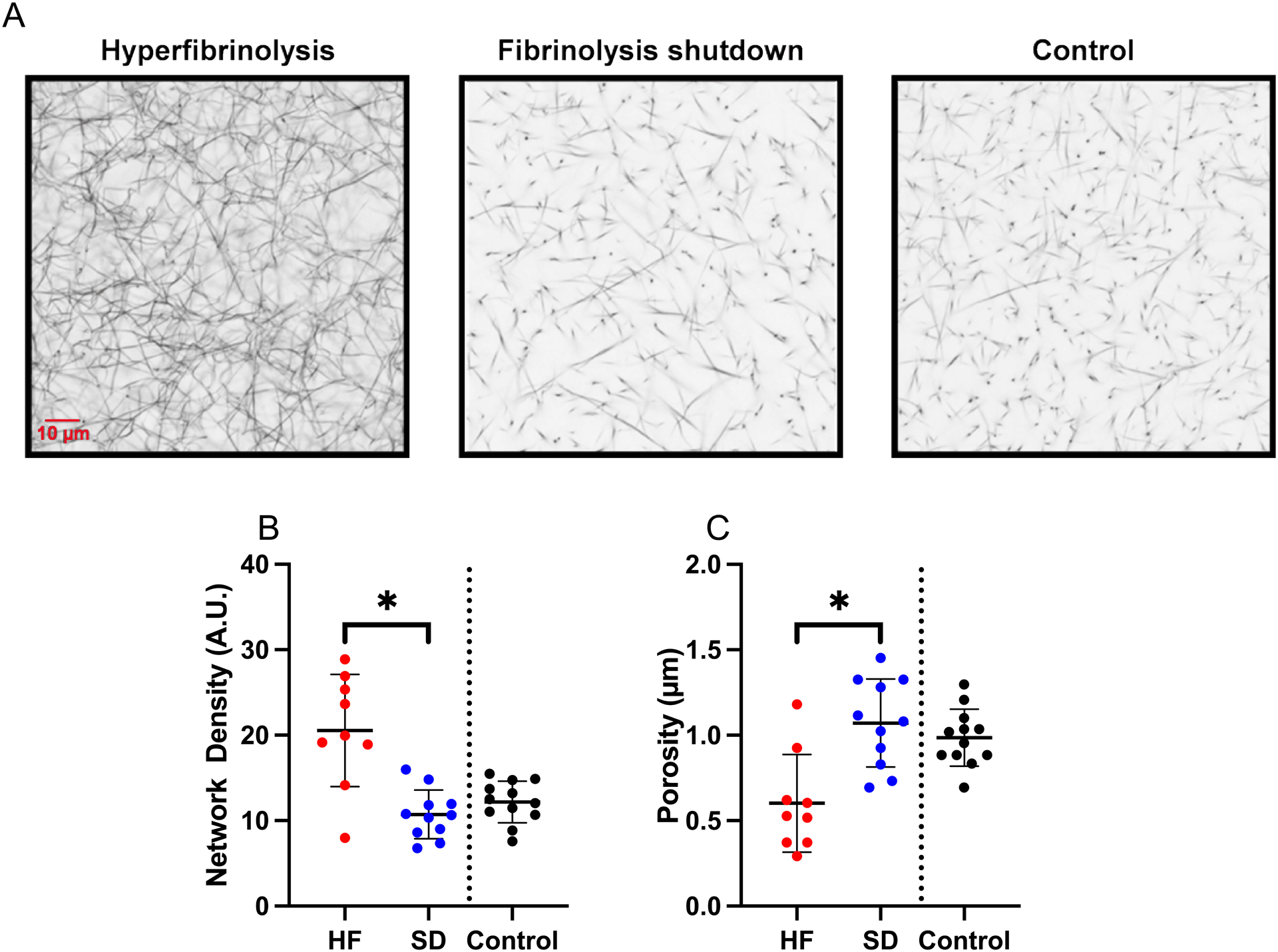
Clot formation was triggered by addition of TF to recalcified plasma and clots were analyzed by confocal microscopy. (A) Representative images showing cross-sections from a three-dimensional Z-stacks of 40 images captured from each clot. (B) Fibrin network density (total fluorescence per clot, Unpaired t-test). (C) Size of pores between fibrin fibers (Unpaired t-test). Healthy controls are shown for comparison, but were not included in statistical analysis. Dots show individual patients, lines show mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05
