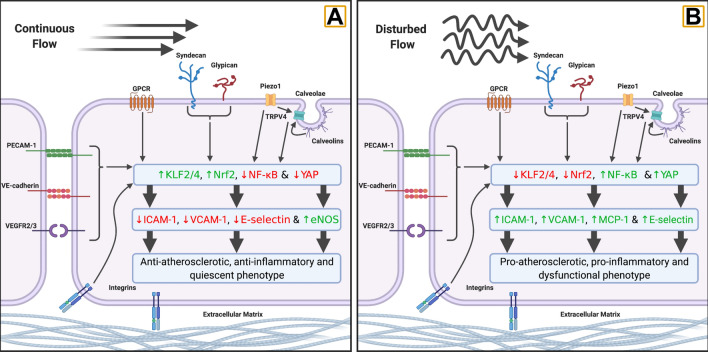
Fig. 3.
Differences in typical response between continuous and disturbed flow models. a Prolonged continuous and elevated flow results in the promotion of a quiescent endothelial cell phenotype through the upregulation of Krüppel-like factor 2 and 4 (KLF2/4) and Nuclear-factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), while suppressing the activity of Nuclear-factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP), via the array of mechanosensory pathways detailed in Fig. 2. b Disturbed flow, characterised by oscillatory patterns of low or reversing shear stress, activates mechanosensory pathways through many of the same receptors as seen in continuous flow; however, these patterns drive opposing responses to those seen in continuous flow leading to the promotion of a dysfunctional endothelial phenotype. Created in BioRender.com