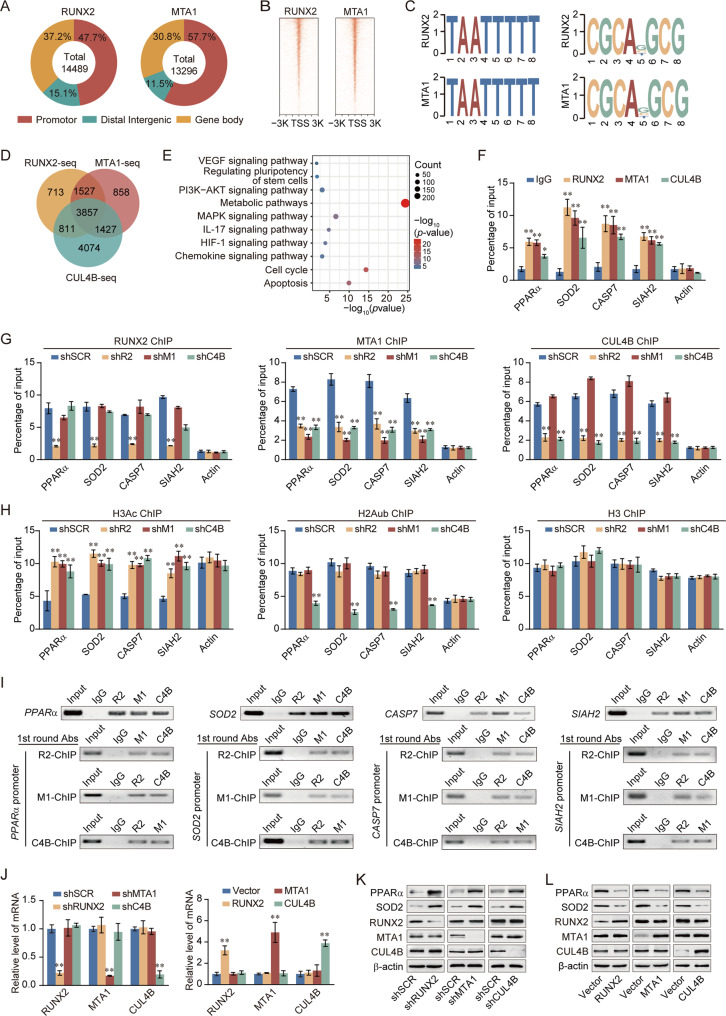
Fig. 5. RUNX2 recruits the NuRD(MTA1)/CRL4B complex for transcriptional repression in breast cancer cells.
A Genomic distribution of RUNX2 and MTA1 determined using ChIP-seq analysis. B ChIP-seq density heatmaps of RUNX2 and MTA1. C RUNX2 and MTA1-bound motifs analyzed using the MEME suite. D Venn diagram of overlapping promoters bound by RUNX2/MTA1/CUL4B complex. E KEGG pathways analysis of 3857 unique genes. F Verification of ChIP-seq results using qChIP analysis of indicated genes. G, H MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with lentiviruses carrying the indicated shRNAs. qChIP analysis of the target gene promoters was performed using antibodies against RUNX2, MTA1, or CUL4B (G) or against histone H3Ac and H2AK119ub1 (H); Histone H3 was detected as an internal control. Results were represented as fold change over control with β-actin as a negative control. I ChIP and Re-ChIP experiments in MDA-MB-231 cells with the indicated antibodies. J Knockdown and overexpression efficiencies of RUNX2, MTA1, or CUL4B verified by RT-qPCR. K, L Western blotting analysis of ChIP-seq indicated genes (PPARα and SOD2) in MDA-MB-231 cells with depletion or overexpression of RUNX2, MTA1, or CUL4B. TSS, transcriptional start site; shR2, shRUNX2; shM1, shMTA1; shC4B, shCUL4B; R2, RUNX2; M1, MTA1; C4B, CUL4B; H3Ac, pan-H3 acetylation; H2Aub, H2AK119 monoubiquitination; 1st round Abs, first round antibodies. All results were presented as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.