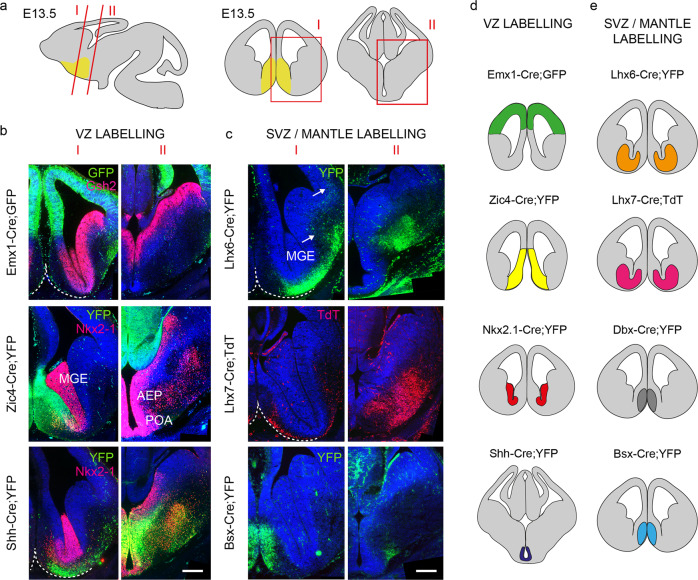
Fig. 2. Transgenic mice used to fate-map the embryonic septum.
a Schematic representation of a sagittal E13.5 mouse brain section and the corresponding coronal cuts shown in I and II. Boxed areas in red are shown for rostral (I) and caudal (II) levels. The position of the septum is indicated in yellow. b YFP/GFP expression in forebrain germinal regions (ventricular zone, VZ) of three lines used for fate mapping. Cre recombination can be detected in the neocortex (Emx1-Cre;GFP), the septum (Zic4-Cre;YFP) and the AEP/POA (Shh-Cre;YFP). Immunolabelling for Gsh2 and Nkx-2-1 delineates the subpallium and the MGE/POA regions, respectively. Scale bar: 200 μm. c Transgenic lines with expression in the subventricular (SVZ) and mantle zones. In Lhx6-Cre;YFP, YFP labelling spans the MGE SVZ and mantle. YFP+ve neurons initiating their migration toward the cortex are indicated with white arrows. TdT expression is detected in presumptive immature cholinergic forebrain neurons in Lhx7-Cre;TdT. YFP immunoreactivity can be detected in the mantle zone of the septum in Bsx-Cre;YFP mice. Ventral boundaries are indicated by a dashed white line. AEP anterior entopeduncular region, MGE medial ganglionic eminence, POA preoptic area. Scale bar: 200 μm. d, e Summary of VZ- and SVZ/mantle-expressing Cre lines used in this study. The area of expression for each transgenic line is identified by a different colour. The same colour coding is used in subsequent fate-mapping Figs. 3–5.