Figure 1.
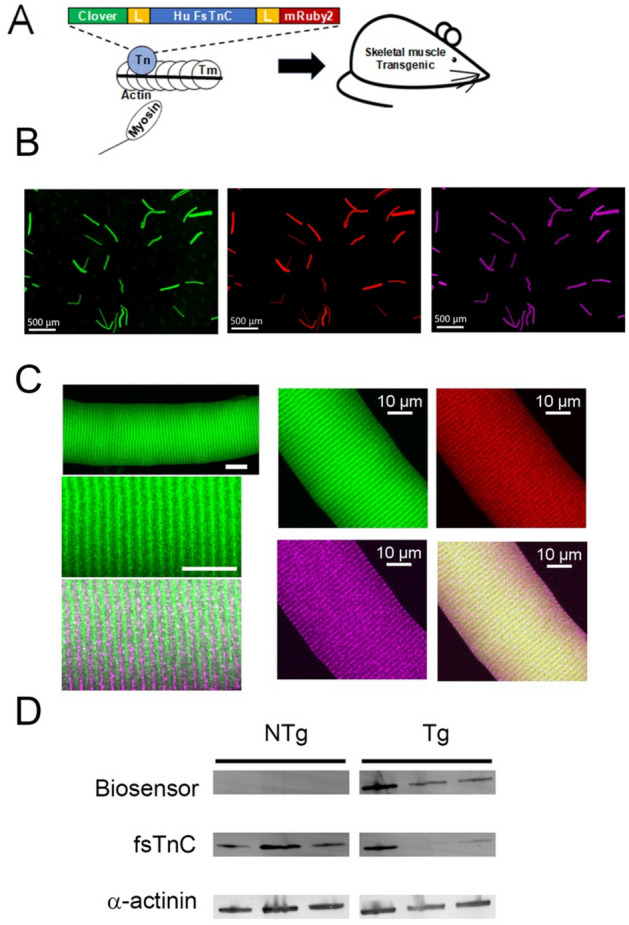
TnC biosensor transgene construction, localization, and expression. (A) The human fast skeletal muscle troponin C (h-fsTnC) cDNA was engineered and flanked on the 5’-end by a 19 amino acid flexible linker and the green fluorescent protein Clover and on the 3’-end by an 8 amino acid flexible linker and the red fluorescent protein mRuby2. (B) Low magnification immunofluorescence images of isolated FDB fibers demonstrating Clover (green) and mRuby2 (red) expression and α-actinin staining (purple) (scale bar = 500 μm). (C) High magnification immunofluorescence images of isolated FDB fibers. Left panel contains confocal images which show myofilament localization of the TnC biosensor (Clover-green, α-actinin – purple) (Top scale bar = 20 μm, bottom scale bar = 10 μm). Right panel images of same FDB fibers demonstrating co-localization of Clover (green) and mRuby2 (red) resulting in yellow (lower right panel) in correct orientation between Z-lines show by α-actinin staining (purple). (D) Western blot of fsTnC expression probed with anti-fsTnC antibody in transgenic EDL myofibers shows stoichiometric replacement of endogenous fsTnC (18 kDa) by the higher molecular weight biosensor fsTnC (72 kDa). The blot was also probed with an antibody for α-actinin (103 kDa) as a loading control. For clarity, the blot has been spliced to remove intervening non-specific bands. The full, labelled, blot is provided in the supplement (Supplementary Figs.1, 2).
