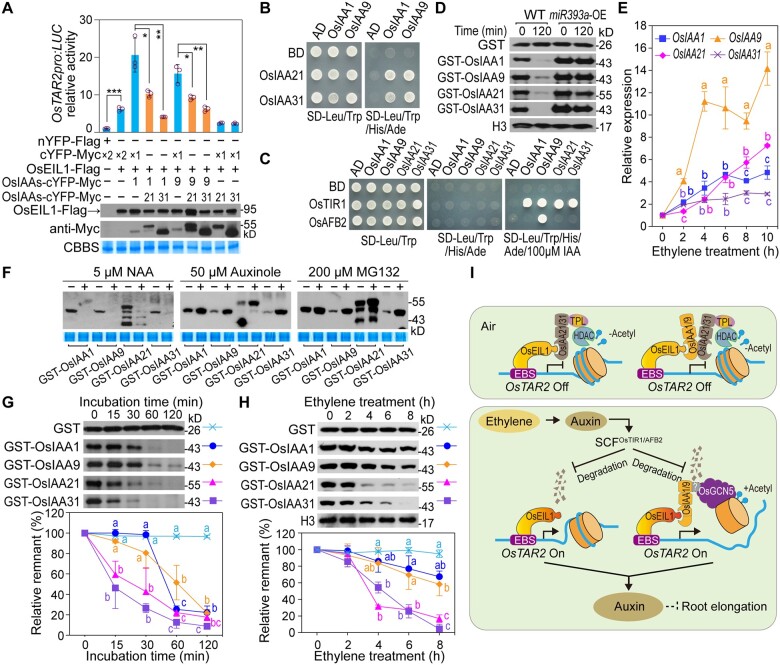
Figure 7.
Interplay between OsIAA1/9/21/31 and OsEIL1 modulates OsEIL1-activated OsTAR2 expression in rice root. A, Roles of OsIAA1/9 and OsIAA21/31 in regulating OsEIL1-activated OsTAR2pro:LUC transcription. Data are means ± sd (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, as determined by a two-tailed Student’s t test compared to the corresponding control. B, Physical interaction between OsIAA1/9 and OsIAA21/31 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. C, Yeast two-hybrid assay for Aux-dependent interaction between OsIAA1/9/21/31 and the Aux receptors OsTIR1/AFB2. D, Degradation of OsIAA1/9/21/31 in root extracts of miR393a OE seedlings. Immunoblot evaluates the amount of the proteins, and histone H3 indicates the identical loading of root crude extracts in each reaction. E, Ethylene-induced expression of OsIAA1/9/21/31 in root tips. Data are means ± sd (n = 3). F, Effects of NAA, auxinole or MG132 treatments on OsIAA1/9/21/31 abundance in root extracts. For auxinole and MG132 treatments, seedlings used for root extracts preparation were pretreated with 10 ppm ethylene for 8 h. Each of the three chemicals or their corresponding solvents were preincubated with root extracts for 10 min, and then recombinant OsIAA was added and incubated for 30 min. G, Degradation of OsIAA1/9 and OsIAA21/31. Free GST protein served as a control. Data are means ± sd (n = 3). H, Comparison of the stability between OsIAA1/9 and OsIAA21/31 in response to ethylene. GST-tagged Aux/IAA proteins were incubated for 30 min with root crude extracts of etiolated seedlings treated with 10 ppm ethylene for different times. Data are means ± sd (n = 3). I, Working model for the OsEIL1-OsIAAs module in the regulation of OsTAR2 expression in root ethylene response. In air, OsEIL1 accumulates at a low level. OsIAA21/31 may interact with OsEIL1 to repress OsEIL1-activated OsTAR2 expression through recruiting the HDAC for potential histone deacetylation. OsIAA21/31 may also suppress the activity of the OsEIL1-OsIAA1/9 complex. OsTAR2 transcription stays at a normal level for basal Aux biosynthesis to sustain normal root growth. Upon ethylene treatment, the induced Aux levels lead to early degradation of OsIAA21/31, thus allowing the promotion of OsEIL1-activated OsTAR2 expression via OsIAA1/9 for signal amplification. The promotive roles of OsIAA1/9 involve the recruitment of the histone acetyltransferase OsGCN5 for histone modification and chromatin activation. Different lowercase letters indicate significance levels of P < 0.05, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (E, G, and H).