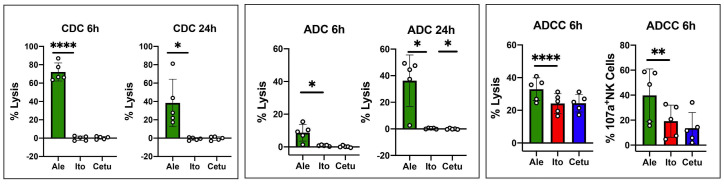
Figure 5.
Testing itolizumab for complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cytotoxicity and antibody direct cellular cytotoxicity. For complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADC), CD3+ T cells were isolated from cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors (HD) and cultured in the presence of medium + antibody + 25% of human serum (HS) and medium + antibody, respectively. Percentage cell lysis was calculated by combining the percentage of positive cells for 7-AAD or Annexin V or both. CDC activity was calculated by subtracting the values obtained in medium + antibody from the values obtained in the culture with medium + antibody + HS. ADC activity was calculated by subtracting the values obtained in the culture with medium alone from the values obtained in the culture with medium + antibody. CDC and ADC were assessed after 6 and 24 hours of culture. For antibody direct cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) PBMC from HD were cultured in the presence of antibody for 6 hours. Both percentage cell lysis and CD107a expression on NK cells were evaluated after 6 hours of culture. The effects of itolizumab (red boxes) were compared to alemtuzumab (green boxes - positive control) and cetuximab (blue boxes - negative control). Values are expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD), paired t-test, 2 tails was used. Statistically significant differences are noted: ****P<0.0001; ***P<0.001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05; paired t-test. HD n=5.