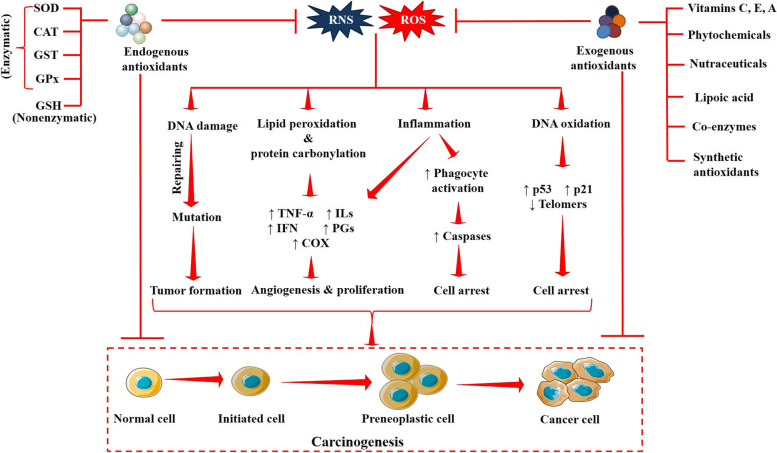
Fig. 3.
Involvement of oxidative radicals in carcinogenesis and chemopreventive role of antioxidants. ROS and RNS endorse carcinogenesis via DNA damage, DNA oxidation, inflammation, and peroxidative damage of cellular macromolecules, which integrally promote tumor initiation, cell arrest, angiogenesis, and proliferation. Red arrows indicate downstream events and red lines indicate inhibition. CAT, catalase; COX, cyclooxygenase; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, glutathione; GST, glutathione S-transferase; IFN, interferon; ILs, interleukines; p21, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21; p53, cellular tumor antigen p53; PGs, prostaglandins; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha