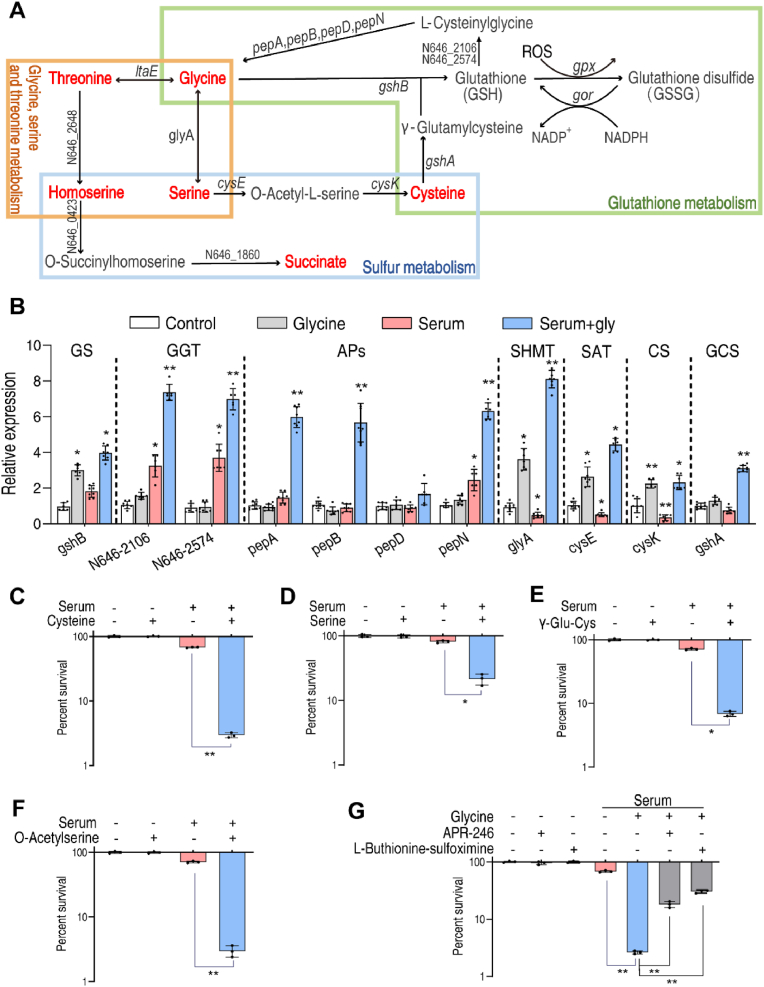
Fig. 3.
Glycine regulates GSH and sulfur metabolism. A. Metabolic pathways for glycine, serine, threonine, sulfur and GSH. Red indicates metabolites increased by glycine. B. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) of genes in GSH and sulfur metabolism. C–F. Percent survival of V. alginolyticus 12G01 in the presence of the indicated concentration of l-cysteine (12.5 mM) (C), serine (100 mM) (D), γ-Glu-Cys (250 μM) (E) and O-Acetylserine (50 mM) (F) plus100 μL serum. G. Percent survival of V. alginolyticus 12G01 in the presence of 100 mM glycine with 100 μL serum in the presence of l-buthionine-sulfoximine (50 mM) or APR-246 (1 mM). GS: GSH synthetase; GGT: gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase; Aps: aminopeptidase; SHMT: serine hydroxymethyl transferase; SAT: serine acetyltransferase; CS: cysteine synthase; GCL: glutamate cysteine ligase. Results are displayed as mean ± standard errors of the means (SEM) (N ≥ 3 technical replicates per sample), and statistically significant differences are identified. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01. Each experiment was repeated independently at least three times. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)