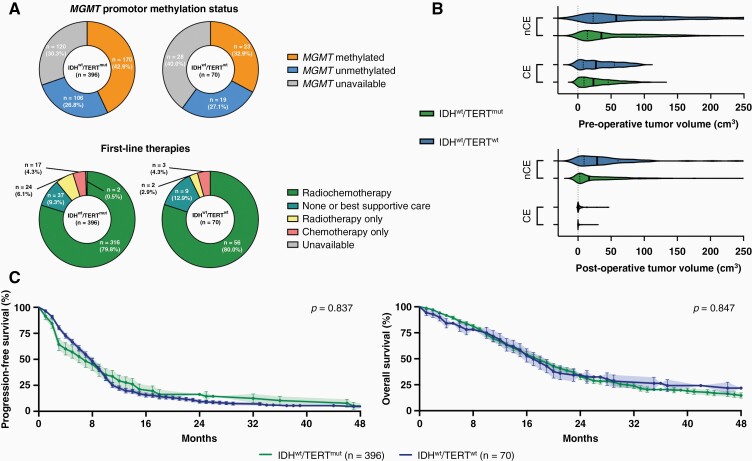
Figure 1.
Clinico-molecular markers and outcome in IDH-wildtype glioblastoma with or without TERT promotor mutations. (A) Distribution of MGMT promotor methylation status (upper panel) and first-line therapies following surgery (lower panel) in IDH-wildtype glioblastomas with (IDHwt/TERTmut; n = 396) or without TERT promotor mutations (IDHwt/TERTwt; n = 70). (B) Pre- (upper panel) and postoperative tumor volumes (lower panel) in cm3 among IDH-wildtype glioblastomas undergoing microsurgical tumor resection with (IDHwt/TERTmut; n = 358; green) or without TERT promotor mutations (IDHwt/TERTwt; n = 63; blue). Volumes are indicated for contrast-enhancing (CE) and noncontrast-enhancing (nCE) tumor tissue. Median ± interquartile range. (C) Kaplan–Meier estimates of progression-free survival (left) and overall survival (right) for IDH-wildtype glioblastomas with (green line) or without TERT promotor mutations (blue line). Points indicate deceased or censored patients; light shadings indicate SEM.