Figure 4.
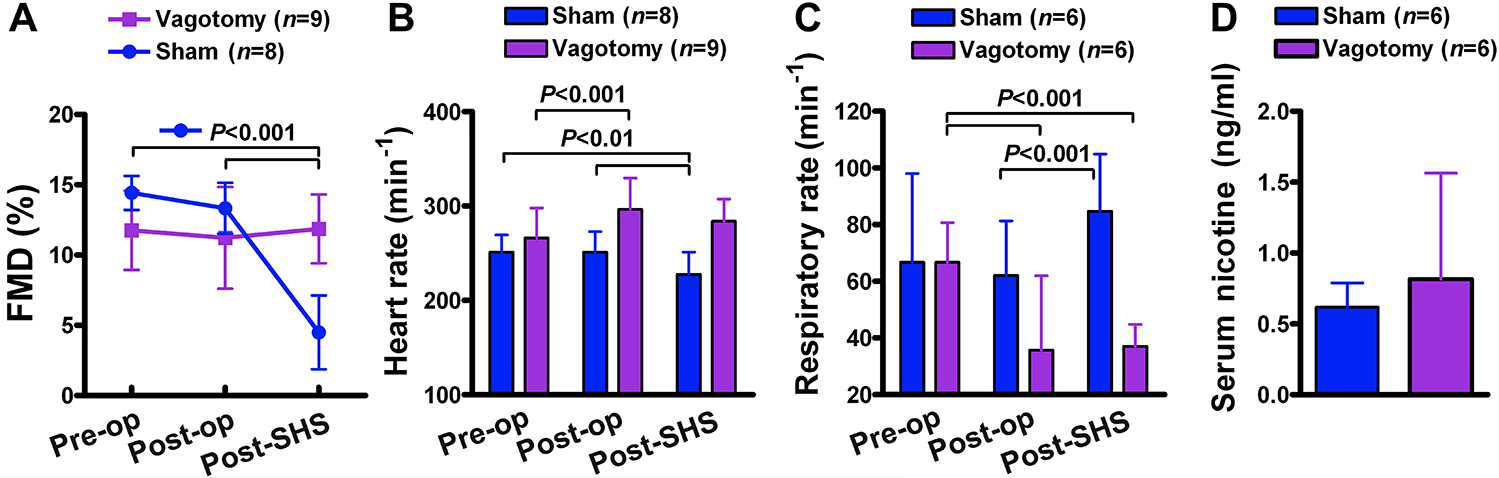
Bilateral cervical vagotomy prevented impairment of FMD by cigarette smoke. Anesthetized rats underwent bilateral cervical vagotomy or sham operation before exposure to 10 min of sidestream smoke. Average starting concentration of respirable suspended particles (RSP) were 790±18 μg/m3 for the vagotomy group and 808±16 μg/m3 for sham-operation group (see Supplemental Figure S3 for decreasing RSP levels over the exposure period. Vagotomy group consisted of 4 male and 5 female (n=9); sham-operation group consisted of 4 male and 4 female (n=8). “Pre-op” = pre-operation, “post-op” = post-operation, “post-SHS” = post-sidestream smoke. Data are mean±SD. (A) Changes in FMD (see Supplemental Figure S4 for breakdown by gender). (B,C) Changes in heart rate and respiratory rate. (D) Serum nicotine at 20 min post-end-of-exposure in subsequent control experiment. Group sizes for panel C are smaller than those in A,B because we did not measure respiratory rate for the first several rats. Group sizes in panel D are the same as those in panel C by coincidence.
