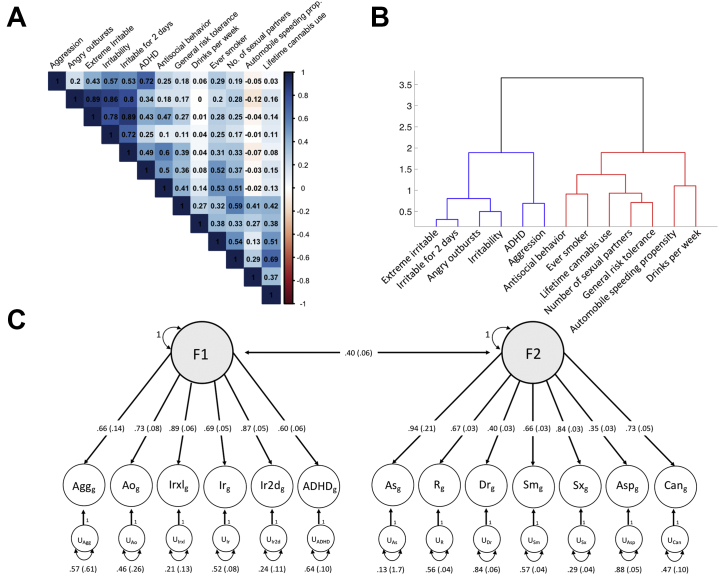
Figure 1.
Genetic factor structure of externalizing behaviors. (A) Genetic correlations between the externalizing phenotypes calculated by linkage disequilibrium score regression. (B) Hierarchical clustering dendrogram based on genetic resemblance of the externalizing phenotypes. Blue represents the disruptive behavior cluster, and red represents the risk-taking behavior cluster. (C) Based on the results of an exploratory factor analysis of the genetic correlations presented in panel (A), a confirmatory factor model with two correlated genetic factors was specified using genomic structural equation modeling. In this model, the common factors account for the genetic covariation among the externalizing traits, i.e., each of the two common genetic factors represents variation in genetic liability that is shared across the phenotypes that load on it. Disruptive behavior represents shared genetic liability among disorders characterized by disruptive behavior, and risk-taking behavior represents the shared liability for risk-taking behavior. One-headed arrows connecting the common genetic factors to the individual traits represent standard loadings, which can be interpreted as coefficients from a regression of the true genetic liability for the trait on the common factor. Two-headed arrows connecting the genetic components represent their correlations. Two-headed arrows connecting the genetic components of the individual traits to themselves represent residual genetic variances and correspond to the proportion of heritable variation in liability to each individual trait that is unexplained by the two factors. ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; Agg, aggression; Ao, angry outbursts; As, antisocial behavior; Asp, automobile speeding propensity; Can, lifetime cannabis use; Dr, drinks per week; Irxl, extreme irritable; Ir, irritability; Ir2d, irritable for 2 days; R, general risk tolerance; Sm, ever smoker; Sx, number of sexual partners.