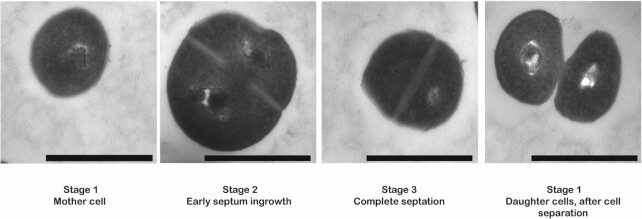
Figure 1.
Different stages in the cell cycle of Staphylococcus aureus as visualized by transmission electron microscopy. During the initial phase of the cell cycle (stage 1), a spherical S. aureus mother cell will become slightly enlarged and forms a septum at the mid-cell position (stage 2). Once the synthesis of the septum is complete and the cell is further enlarged (stage3), bacterial autolytic enzymes will promote cell division, resulting in two daughter cells (stage 1). After cell separation, the septum of the daughter cells is reshaped from a flat surface into a hemisphere. Images were recorded by transmission electron microscopy. The magnification is indicated by scale bars (1 μm).