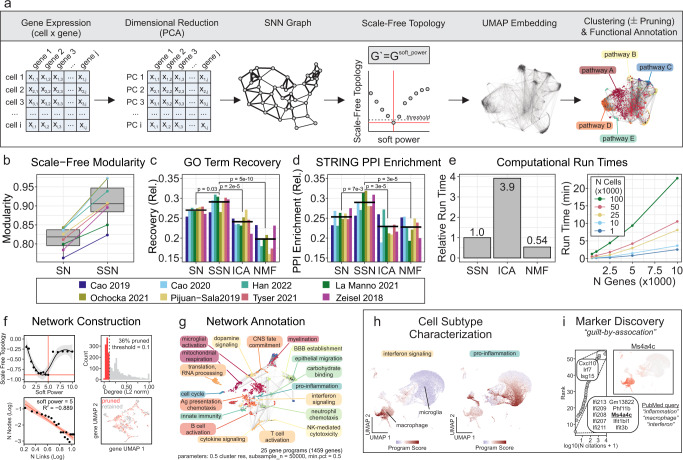
Fig. 5. Gene program discovery using scale-free shared nearest neighbor network (SSN) analysis.
a Schematic illustrating network construction and annotation. b Network modularity with (SSN) and without (SN) scale-free topology enforcement. c–e Comparison of GO term recovery (c), STRING PPI enrichment (d) and computational run time (e) across different gene program discovery methods. ICA; independent component analysis, NMF; non-negative matrix factorization, SN; shared nearest neighbor network, SSN; scale-free shared nearest neighbor network. (f–i) Representative transcriptional network construction, annotation and applications using Ochocka 2021 scRNA-seq data25. f Optimal soft power required for scale-free topology (left column; threshold = −0.9) and pruning of genes with low network connectivity (right column; threshold = 0.1). g Functional annotation of gene programs. GO term enrichment was performed using hypergeometric overrepresentation analysis. h Activity of “interferon signaling” and “pro-inflammation” programs overlaid on cell UMAP. Macrophage and microglial subpopulations can be subtyped by program activity status. i Marker discovery and functional prediction using guilt-by-association. Genes belonging to “interferon signaling” program were cross-referenced with PubMed articles queried using “inflammation”, “macrophage” and “interferon” search strings to identify candidate genes (e.g., Ms4a4c) implicated in interferon signaling. Ms4a4c expression was visualized on a UMAP to verify that expression is coherent with gene program activity.