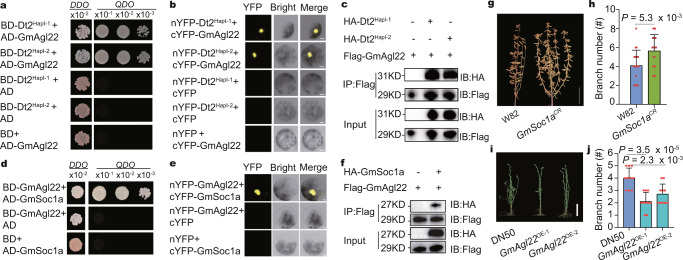
Fig. 3. Dt2, GmAgl22 and GmSoc1a could interact with each other and affect the branch number.
a Interaction between Dt2 and GmAgl22 in the yeast two-hybrid assay. Transformed yeast cells are grown on DDO (Trp/Leu) or QDO (Trp/Leu/His/Ade) synthetic dropout medium. The number at the top indicates three serial dilutions. AD, GAL4 activation domain; BD, GAL4 DNA-binding domain. b BiFC analysis of the interaction between Dt2 and GmAgl22. Scale bars, 10 mm. cYFP C-terminal portion of YFP. nYFP N-terminal portion of YFP. c Co-IP analysis of the protein interactions between Dt2 and GmAgl22. Flag-tagged GmAgl22 is co-transformed with HA-tagged Dt2 into Arabidopsis protoplasts. d Interaction between GmSoc1a and GmAgl22 in the yeast two-hybrid assay. e BiFC analysis of the interaction between GmSoc1a and GmAgl22. Scale bars, 10 mm. f Co-IP analysis of the protein interactions between GmSoc1a and GmAgl22. g Phenotypic comparison between W82 and GmSoc1aCR lines. Scale bars, 20 cm. h Branch number statistic in W82 and GmSoc1aCR lines (n = 20 biologically independent plants). i Phenotypic comparison between DN50 and GmAgl22OE lines. Scale bar, 10 cm. j Branch number statistic in DN50 and GmAgl22OE lines (n = 10 biologically independent plants). All the data in the graphs represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance is determined using a two-sided t-test. For (b, e), at least 5 independent cells are observed and a representative result is shown. For (c, f), at least 3 independent replicates are performed and a representative result is shown. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.