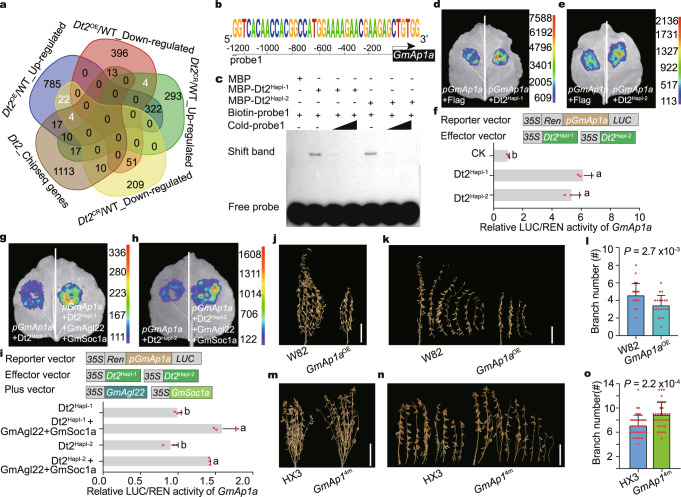
Fig. 4. Dt2 directly binds the promoter of GmAp1a and positively regulates its expression.
a Venn diagram among overlapping DEGs from DN50, Dt2CR and Dt2OE lines. b A probe sequence that could be bound by the MADS-box protein in the promoter of the GmAp1a is predicted in Plantpan (http://plantpan.itps.ncku.edu.tw/). c MBP-Dt2HapI-1 or MBP-Dt2HapI-2 directly bind to the promoter of GmAp1a in EMSA. MBP, maltose-binding protein. At least 3 independent replicates are performed and a representative result is shown. d, e Transient dual luciferase (dual-LUC) assays of Dt2HapI-1 (d) and Dt2HapI-2 (e) binding to the promoter of GmAp1a in tobacco leaves. f Transient dual luciferase (dual-LUC) assay of Dt2 on the promoter of GmAp1a in Arabidopsis protoplast (n = 3 biologically independent replicates). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences at P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA test. g, h Transient dual-LUC assay in tobacco leaves of Dt2HapI-1 (g) or Dt2HapI-2 (h) and its interacting proteins GmAgl22 and GmSoc1a on the promoter of GmAp1a. i Transient dual-LUC assay of Dt2 and its interacting proteins GmAgl22 and GmSoc1a on the promoter of GmAp1a in Arabidopsis protoplasts (n = 3 biologically independent replicates). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences at P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA test. j, k Phenotypic comparison between W82 and GmAp1aOE lines. Scale bars, 20 cm. l Branch number statistics of W82 and GmAp1aOE lines (n = 20 biologically independent plants). Statistical significance is determined using a two-sided t-test. m, n Phenotypic comparison between the HX3 and GmAp14m mutation lines in branch number. Scale bars, 20 cm. o Branch number statistics of the HX3 and GmAp14m mutation lines (n = 20 biologically independent plants). Data in (f, i, l and o) are mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.