Fig. 7.
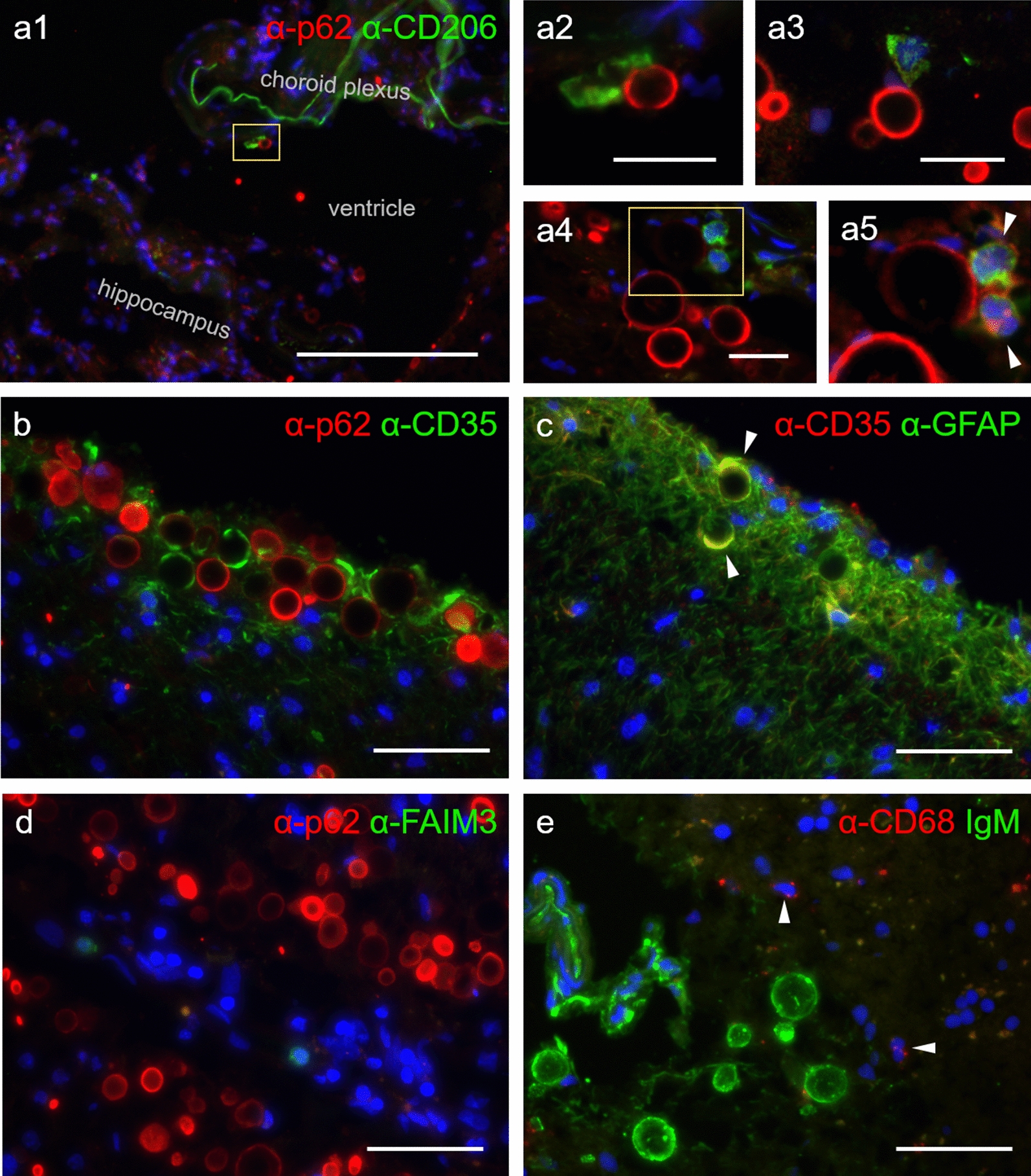
Some macrophages at central nervous system interfaces interact with wasteosomes. a1, a2, a3, a4 and a5 wasteosomes from human hippocampal sections immunostained with anti-p62 (red) and interface macrophages immunostained with anti-CD206 (green). a1 A choroid plexus macrophage in contact with a wasteosome released from the brain tissue to the ventricular CSF. a2 inset of a1, where the macrophage attached to the wasteosome is magnified. a3 and a4 wasteosomes released from hippocampus to the subarachnoid space in contact with meningeal macrophages. a5 inset of a4, where the red staining is digitally intensified to evidence the presence of a wasteosome, in this case surrounded by two macrophages (white arrowheads). b within the brain parenchyma, wasteosomes become immunostained with anti-p62 (red) and are surrounded by CD35 + cells (green). c CD35 staining (red) colocalize with GFAP staining (green, white arrowheads), indicating that cells that surround wasteosomes are CD35 + astrocytes. d wasteosomes from human hippocampus immunostained with anti-p62. FAIM3 positive cells are not found in the hippocampal sections (green). e wasteosomes from human hippocampal tissue immunostained with IgMs (green) are not contacted by CD68 + cells (red, marked with white arrowheads). For their localization, these CD68 + cells are presumably microglial cells, although possible infiltrating macrophages cannot be discarded. In any case, and as expected, microglia or macrophages did not reach the wasteosomes within the brain parenchyma since in this region wasteosomes are intracellular astrocytic structures. Scale bar in a1: 200 µm; scale bars in a2, a3 and a4: 25 µm; other scale bars: 50 μm. Hoechst (blue) was used for nuclear staining
