Figure 1.
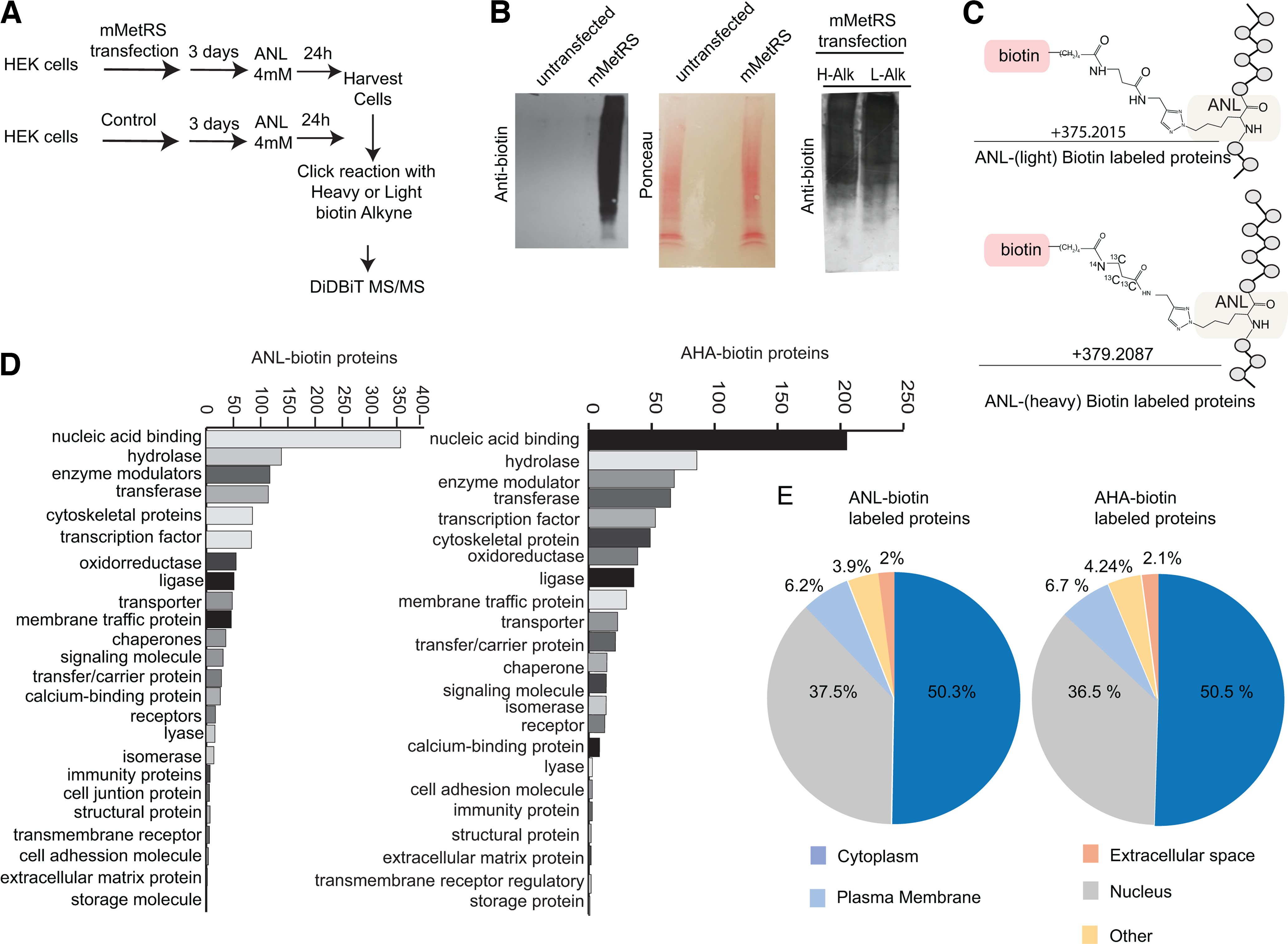
Direct detection of newly synthetized ANL-biotin-labeled proteins in mMetRS expressing HEK293T cells. A, Protocol for in vitro ANL labeling. HEK cells were transfected using lipofection with mMetRS and incubated with 4 mm ANL in methionine-free media for 24 h. Cell pellets were washed, homogenized, and processed for click chemistry with heavy or light biotin alkyne. After click reactions, proteins were precipitated and digested, and ANL-biotin-tagged peptides were isolated on NeutrAvidin using the DiDBiT protocol. B, Left, mMetRS-transfected cells, but not untransfected cells, showed incorporation of ANL. Western blots for biotin (left) and corresponding Ponceau staining (right). Right, Western blots of ANL-biotin-tagged proteins from click reactions performed with heavy or light biotin-alkyne show comparable biotin labeling. H-Alk, heavy-alkyne; L-Alk, light-alkyne. C, Chemical structure of the ANL-biotin modification on methionine sites in peptides, with +375.2015 and +379.2087 mass gain for light and heavy biotin-alkynes, respectively, used for direct mass spectrometry identification of tagged peptides. D, Comparable representation of protein classes in ANL-labeled and AHA-labeled newly synthesized proteins using Panther (Extended Data Fig. 1-1, see for proteins in the different categories). E, Comparable subcellular distribution of newly synthesized proteins labeled by ANL and AHA incorporation, according to Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (Extended Data Fig. 1-1, lists of proteins).
