Figure 8.
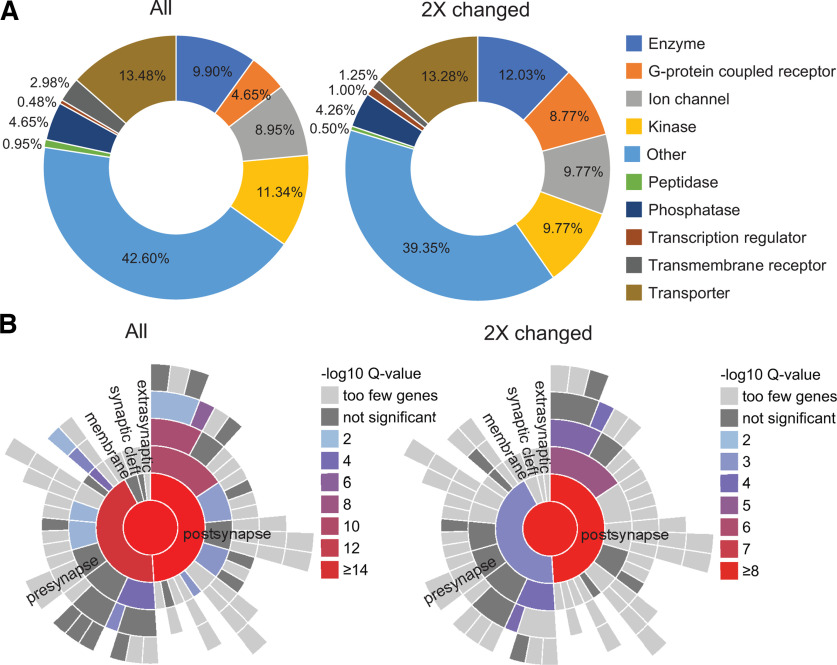
Analysis of activity-induced NSPs annotated to different subcellular compartments. A, Doughnut charts showing the relative representation of functional categories of plasma membrane proteins (as annotated by QIAGEN IPA software) in the entire dataset of proteins (All, left) compared with the subset of proteins that were changed at least twofold in response to the PTZ treatment (2× changed, right). Among the more than twofold changed proteins following PTZ treatment, plasma membrane G-protein-coupled receptors and plasma membrane-associated transcriptional regulators showed the highest proportional increase. Peptidases and transmembrane receptors were decreased, and phosphatases and transporters were largely unchanged by PTZ treatment (Extended Data Figs. 8-1, 8-2). B, Activity-induced synaptic NSPs are enriched in postsynaptic proteins. SynGO, a tool focused on synaptic gene ontologies, showed enrichment of diverse proteins with known synaptic functions in our dataset. The distribution of presynaptic versus postsynaptic newly synthesized proteins was heavily skewed toward postsynaptic proteins in the more than twofold changed dataset (right) compared with the entire dataset (left), indicating that PTZ treatment altered the expression of more postsynaptic proteins than presynaptic proteins (Extended Data Figs. 8-3, 8-4, 8-5, 8-6).