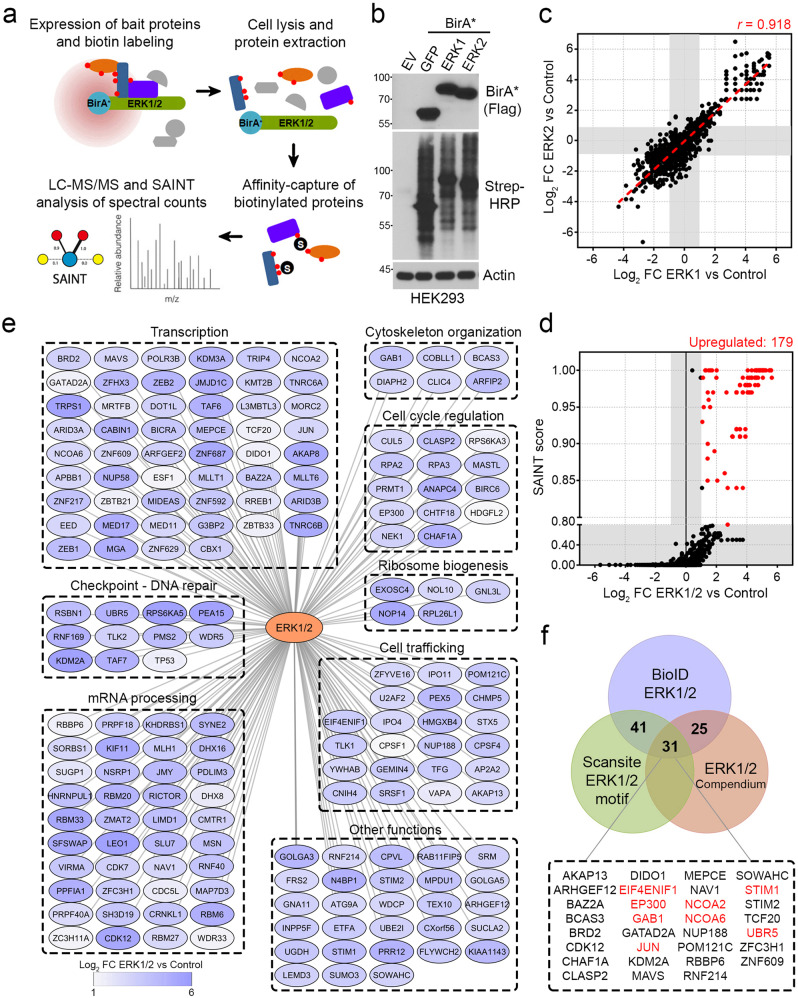
Fig. 1. Characterization of the proximity interactome of ERK1 and ERK2.
a Schematic representation of the proteomics approach used (BioID, proximity-dependent biotin identification) to characterize the proximity interactome of ERK1 and ERK2. b The expression of each transfected bait (BirA-GFP, BirA-ERK1 and BirA-ERK2) in HEK293 was assessed by immunoblotting against the Flag epitope. As cells were also labeled with biotin (50 µM, 24 h), global proximity biotinylation was evaluated by immunoblotting using Streptavidin-HRP. EV empty vector. c Correlation plot between ERK1 and ERK2 proximity interactors identified by BioID. Shaded areas represent cut-off range of Log2 FC (ERK1 versus Control, or ERK2 versus Control). The r = 0.918 value was determined using Pearson correlation. d Global ERK1/2 proximity interactors identified by BioID. Shaded areas represent cut-off range of SAINT score and Log2 FC (ERK1/2 versus Control). e Network of the ERK1/2 proximity interactome organized by biological processes found to be significantly enriched. f Venn diagram representing the overlap between ERK1/2 proximity interactors identified by BioID (this study), and proteins containing a predicted ERK1 motif (kinase and binding site, Scansite 4.0) or present in the ERK1/2 target protein compendium (http://sys-bio.net/erk_targets/). Proteins listed in red are known ERK1/2 substrates. Data are from n = 3 (b, c) and n = 6 (d) independent experiments. d–f Only preys identified by BioID with a SAINT Score ≥ 0.8, BFDR ≤ 0.05 and Log2 FC ≥ 1 were considered. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.