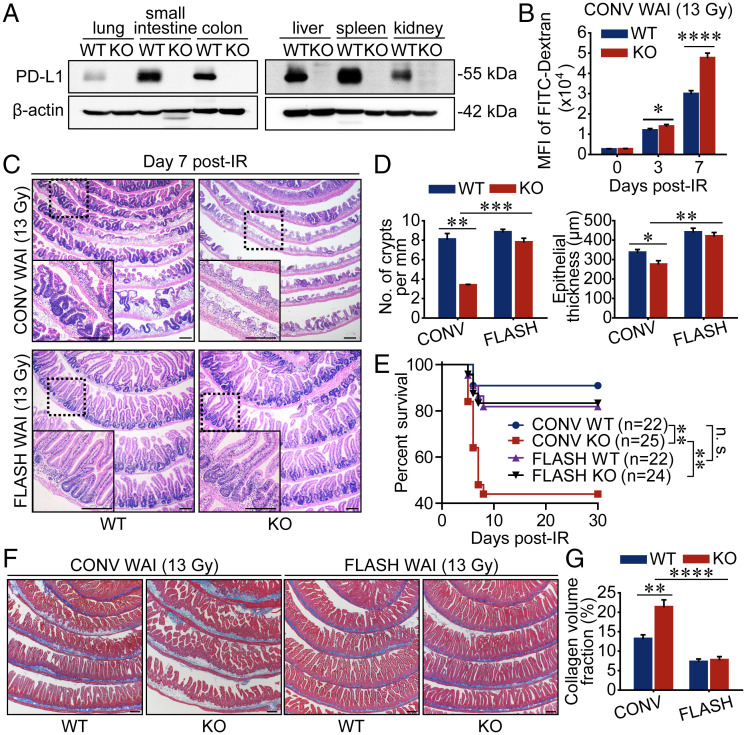
Fig. 1.
FLASH X-ray minimizes mouse enteritis in the context of PD-L1 blockade. (A) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 expression levels in various organs from WT and PD-L1–deficient mice. (B) The gut permeability of mice undergoing 13-Gy CONV WAI was determined by detecting the intensity of fluorescence of FITC-dextran (n = 6 mice per group). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (C and D) Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of proximal intestines sampled at 7 d after 13-Gy WAI are shown (C), and the numbers of crypts per millimeter and epithelial thickness were quantified (D) (n = 3 mice per group). (E) WT and PD-L1 KO mice were exposed to 13-Gy CONV or FLASH WAI. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of mice was performed. (F and G) Representative pictures of Masson-stained sections of proximal intestines sampled at 6 mo after 13-Gy WAI are shown (F), and intestinal fibrosis was quantified by Image J (G) (n = 6 mice per group). Data represent three (A–D) or two (E–G) independent experiments. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, and no significance (n.s.) were determined by a two-sided Student’s t test (B, D, and G) or determined by a log-rank test (E). (Scale bars, 200 μm.)