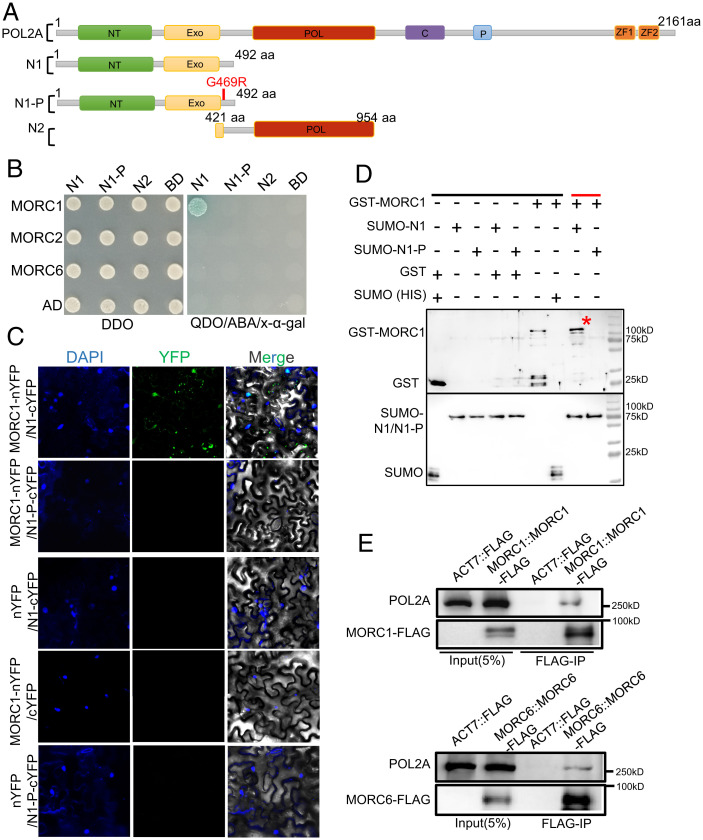
Fig. 2.
N terminus of POL2A interacts with ATPase MORC1. (A) Diagrams showing the full-length, truncated forms and point mutation of AtPOL2A. NT, N terminus; EXO, 3‘-5′ exonuclease; POL, 5‘-3′ polymerase; C, central; P, proliferating cell nuclear antigen interaction. (B) Y2H assay showing N-terminal (N1) POL2A interaction with MORC1, but not MORC2 or MORC6. N1-P is the G469R point mutation adjacent to the EXO-domain of POL2A indicated in A. DDO indicates SD/–Leu/–Trp medium, whereas QDO refers to SD/–Ade/–His/–Leu/–Trp medium. Blue dot refers to positive interaction. (C) Verification of POL2A and MORC1 interaction by BiFC assay. (D) Interaction between POL2A and MORC1 demonstrated using an affinity purification pull-down assay. MORC1::GST and N1-POL2A::SUMO-HIS were precipitated using Ni-NTA beads. Black line indicates input and negative control, and red line indicates the experimental group. Red asterisk indicates the GST-MORC1 band. (E) Co-IP of POL2A with MORC1-FLAG/MORC6-FLAG plants overexpressing FLAG as controls. aa, amino acid; ABA, Aureobasidin A; YFP: Yellow Fluorescent Protein; n/cYFP: n/c terminus of YFP; GST, glutathione S-transferase; SUMO (HIS), Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier-polyhistidine fusion tags.