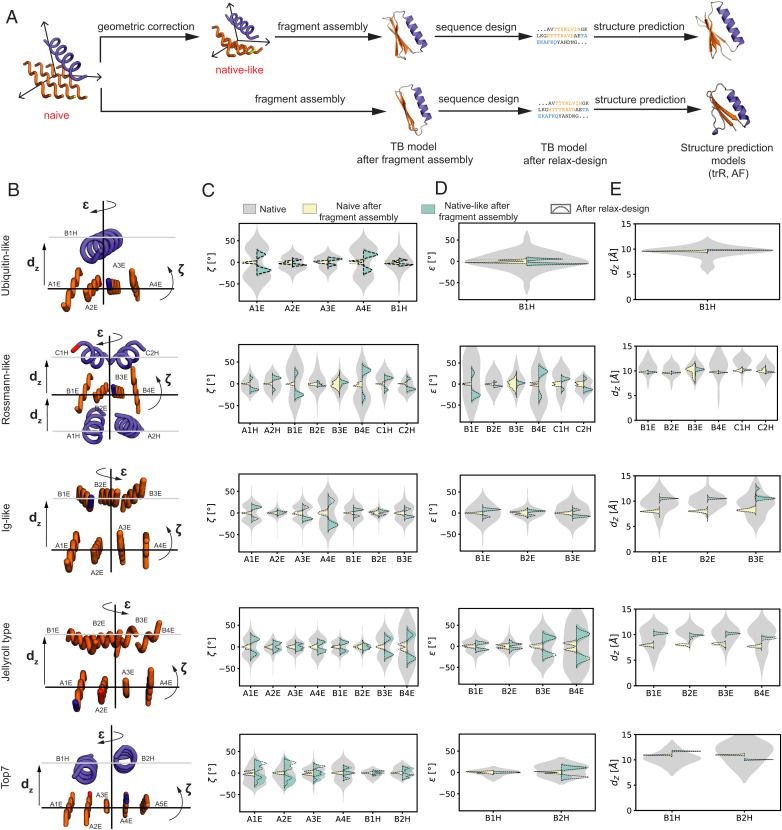
Fig. 3.
Geometric corrections improve topological features of the designed structures. (A) Overview of the naive and native-like TopoBuilder design pipeline. The developed pipeline includes a topological correction step rendering a naive sketch into a native-like structure with improved designability. Full atomistic models are generated through the Rosetta fragment assembly protocol (Rosetta FunFolDes), sequences are designed using the Rosetta FastDesign method and state-of-the-art protein structure prediction methods (trRosetta and AlphaFold) are used to assess the design quality. (B) The native-like sketches of the example folds with three of the geometric parameters indicated. (C) Distributions of the ζ-correction parameter computed from the retrieved matches. The ζ-correction parameter captures features related to the orientation of the different layers. (D) Distributions of ɛ-correction parameter computed from the retrieved matches. The ɛ-correction parameter captures features related to the orientation of the different layers. (E) Distributions of the dz correction parameter computed from the retrieved matches. The dz correction parameter captures the distance between layers in the sketch. (C–E) The native geometry distributions are shown in gray. In yellow, the output of simulations (1,000 decoys) using a naive sketch without correction of the SSEs, which tends to result in flat β-sheets and α-helical stackings. Shown in green are simulations (1,000 decoys) derived from native-like sketches where the outputs more closely follow the native distributions.