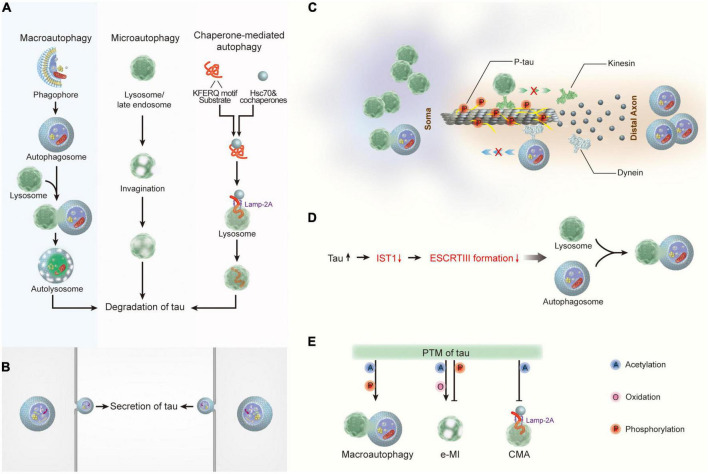
FIGURE 2.
The crosstalk between tau and autophagy. (A) Macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy are involved in tau degradation in neurons. (B) Tau protein can be secreted via the autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway. (C) Pathological tau reduces its binding affinity to microtubules, thereby leading to microtubule depolymerization and the impairment of both the degradative lysosome transportation to axons and the retrograde transport of autophagosomes to lysosomes. (D) Tau accumulation disrupts autophagosome-lysosome fusion via inhibiting IST1 expression and disrupting ESCRT-III complex formation. (E) Post- translational modifications of tau regulate its degradation by autophagy. Hsc70, heat shock cognate 70; Lamp-2A, lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2A; ESCRT, the endosomal sorting complex required for transport; IST1, IST1 factor associated with ESCRT-III; e-MI, endocytic microautophagy; CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy.