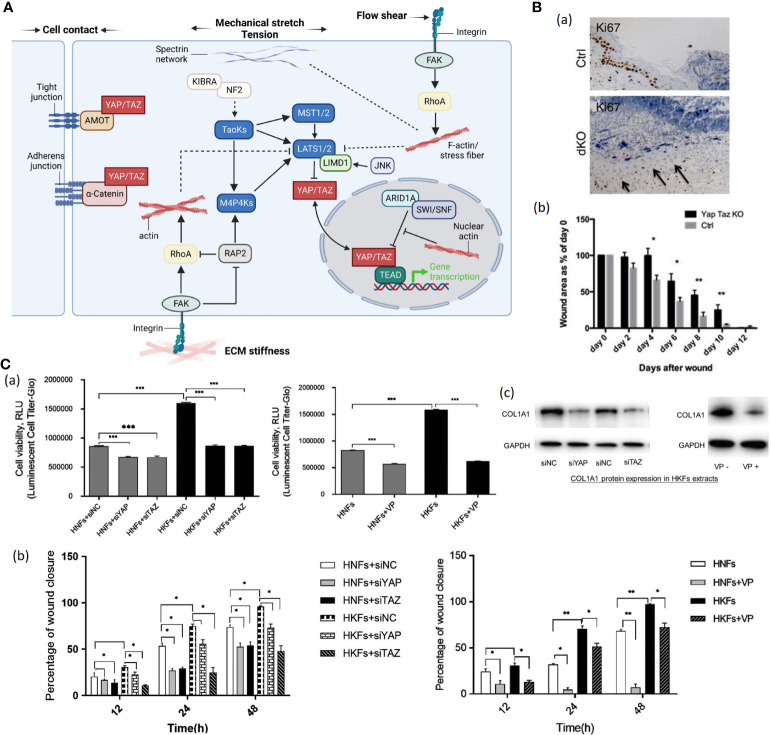
Figure 4.
(A). The schematic diagram YAP/TAZ signaling. Mechanical cues control YAP/TAZ activity through both Hippo-dependent and -independent pathways (78). (1) In response to cell-cell contact, AMOT directly binds to YAP and thus sequesters YAP at tight junctions (78). Adherens junction protein E-cadherin trans-dimerize and subsequently inactivate YAP/TAZ through the MST1/2-LATS1/2 kinase cascade (78). (2) ECM stiffness transducted via Integrin-FAK signaling promotes actin polymerization and stress fiber formation, subsequently inactivating the Hippo kinase cascade (78). Polymerized nuclear actin binds to ARID1A-SWI/SNF complex, relieving its sequestration of YAP/TAZ (78). Stiffness-regulated GTPase RAP2 activates MAP4Ks and inhibits Rho GTPases, inducing inhibitory action of LATS1 and LATS2 kinases on cytoplasmic YAP/TAZ (78). Stiffness-activated JNK phosphorylates LIMD1, which binds to LATS1/2, and activates YAP/TAZ (78). (3) Mechanical stretch or tension modulates YAP/TZ activities through actin cytoskeleton as well (78). Spectrin, a cytoskeletal protein, plays a crucial role in connecting the cellular tension-sensing system to the Hippo regulation network (78). (4) Flow shear patterns and speeds regulate the Hippo kinase cascade activity in endothelial cells via an integrin–Gα12/13–RhoA axis, respectively (78).(Created with BioRender.com). (B) (a) Proliferation of cells marked by Ki67 staining is reduced in dKO wounds versus control animals. Values are means ± s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (79). (b) Quantification of wound healing rates at each stage in control versus dKO animals (79). (C) (a) (Left) Human keloid fibroblasts (HKFs) had increased metabolic activity demonstrated by high RLU value than human normal fibroblasts (HNFs) (n = 3) (80).(Right) Knockdown of YAP or TAZ and verteporfin treatment decreased cell metabolic activity in both HNFs and HKFs (n = 3) (80). (b) (Left) Quantification of cell migration from 3 separate experiments after knockdown of YAP or TAZ in both HNFs and HKFs (80). (Right) Quantifying cell migration from 3 separate experiments to test verteporfin’s effect on HNF and HKF migration (80). VP, verteporfin; siNC, siRNA control; HNFs, human normal fibroblasts; HKFs, human keloid fibroblasts; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (c) (Left) Western blot shows reduced protein expression of COL1A1 in HKFs after siRNA interference (80). (Right) Western blot shows COL1A1 protein expression in HKFs without verteporfin (VP-) and with verteporfin (VP+) treatment (80). ***P < 0.001.