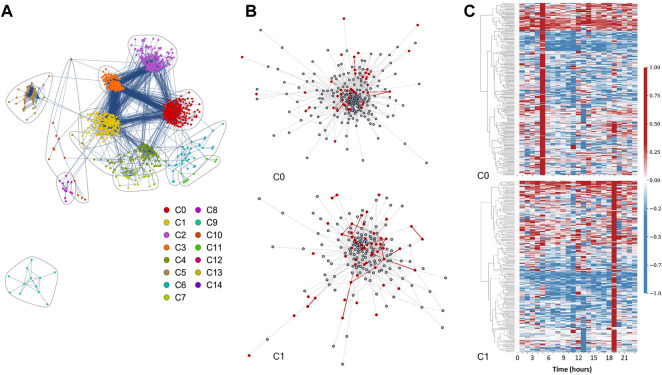
FIGURE 2.
Differential network analysis for the saliva experiment. (A) Differential network with community structure found by the Louvain community detection method. (B) Isolated visualizations of C0 (top) and C1 (bottom) communities with red highlights indicating genes found in statistically significant Reactome pathways (FDR<0.05), and their corresponding edges in the network. (C) Heatmaps of C0 (top) and C1 (bottom) over 24 h. Columns represent time points while rows denote gene identifiers. The row data show the difference in each entry’s expression relative to time 0. The relative values were determined by subtracting the individual time points from time point 0 and then normalizing using a Euclidean norm, so that each row ranges from -1 (down-regulation) to 1 (up-regulation). For the dendrogram clustering we used the complete-linkage method (also known as the Farthest Point Algorithm) Defays (1977); Hartigan (1985).