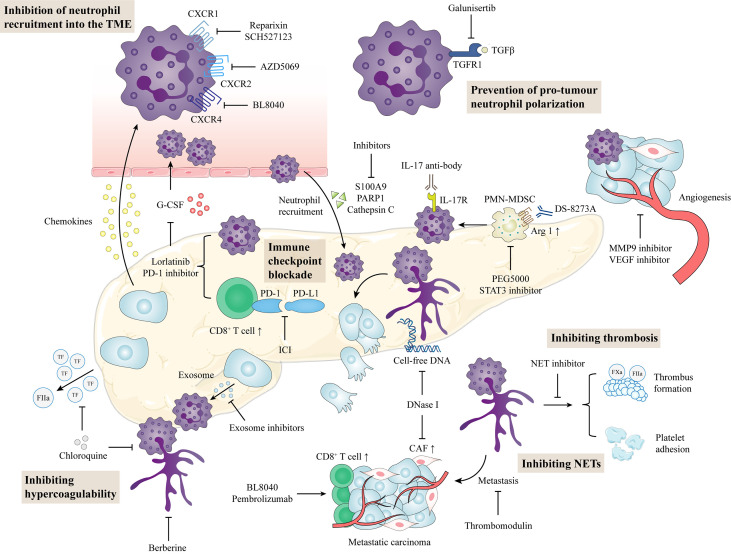
Figure 3.
Potential neutrophil-directed therapeutic targets in pancreatic cancer. Inhibition of chemokines and cytokines prevents neutrophil activation and recruitment, thereby reducing neutrophils in the TME. TGF-β inhibitors can reduce the tumor-promoting phenotype of neutrophils. In the TME, targeting neutrophil combined with immune checkpoint blockade can enhance the antitumor function in pancreatic cancer. NET inhibitors prevent cancer cell metastasis, circulating hypercoagulable states, and venous thrombosis formation. TME, tumor microenvironment; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblasts; PD-L1, programmed cell death-ligand 1; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PMN-MDSC, polymorphonuclear-myeloid derived suppressor cell; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap.