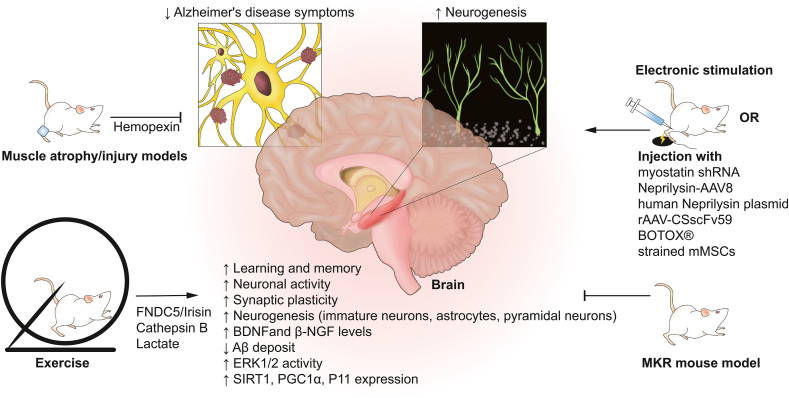
Fig. 3.
Pre-clinical evidences of the highway from muscle to brain. Muscle atrophy/injury animal models and diabetic MKR mouse (muscle insulin resistance) showed cognitive dysfunction and abnormal neurogenesis. Exercise, electronic stimulation, intramuscular injection of muscle-targeted agents attenuated symptoms of Alzheimer's disease and enhanced the neurogenesis, especially in hippocampus. The transport of muscle-secreted hemopexin after atrophy and FNDC5/Irisin, Cathepsin B, as well as lactate after exercise played roles in the brain.